Introduction
In the not-so-distant past, giants of the industry have found themselves entangled in the web of regulatory missteps. The fallout was swift and unforgiving. Financial institutions, once pillars of stability, stumbled as regulatory oversights led to colossal fines and tarnished reputations, and the Lehman Brothers fiasco still rings fresh in our minds.
Consider the tech juggernauts, once soaring on the wings of innovation. In the wake of compliance lapses, their meteoric rise faced abrupt interruptions as legal battles and public scrutiny cast shadows over their technological prowess. All of this might make compliance seem like an arduous task, when in fact it could help stop these very mishaps from taking place. The reverberations of these real-world examples serve as cautionary tales, underscoring the paramount importance of Compliance Management Systems in the modern enterprise.
What is a Compliance Management System?
A compliance management system (CMS) is a structured framework that enables organizations to adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical requirements by implementing policies, procedures, and controls. It helps identify, assess, and mitigate compliance risks while ensuring operational integrity. In a dynamic regulatory environment, a CMS simplifies compliance efforts, enhances accountability, and minimizes the risks of non-compliance.
In the ever-evolving regulatory landscape, enterprises grapple with an increasing number of rules and standards. A CMS acts as a centralized hub, streamlining compliance efforts and mitigating the complexities associated with regulatory adherence.
Who Needs a Compliance Management System?
The need for a robust Compliance Management System transcends industry boundaries, as organizations of all sizes grapple with the growing intricacies of compliance. In the GRC space, the focus is on enterprises that are subject to a multitude of regulations, standards, and internal policies. This includes but is not limited to financial institutions, healthcare providers, energy companies, and those in the technology sector.
Experts at MetricStream unanimously agree that organizations that fit into one or more of these criteria should consider investing in a compliance management system.
- Organizations that are subject to greater regulatory scrutiny either by virtue of their industry of operation (such as BFSI), or due to milestone events such as going public.
- Organizations with large and diverse teams spread across geographies, and having internal structures that are different among teams.
- Companies where compliance or lack thereof has led to significant issues in the past, either due to a lack of awareness, or due to oversight from some teams.
What Is the Purpose of a Compliance Management System?
A compliance management system (CMS) plays a crucial role in helping organizations adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards while minimizing risks. It provides a structured approach to compliance, ensuring that businesses operate within established guidelines and avoid penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Below are the key purposes of a CMS:
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
A CMS helps organizations stay compliant with industry-specific laws, governmental regulations, and international standards. It monitors updates in legal requirements and ensures policies and processes align with changing compliance landscapes.
2. Mitigating Compliance Risks
Non-compliance can lead to financial losses, legal actions, and reputational harm. A CMS identifies, assesses, and mitigates compliance risks by implementing controls, automating monitoring, and ensuring adherence to protocols.
3. Standardizing Policies and Procedures
Organizations operate more efficiently when they have well-defined compliance policies. A CMS ensures consistency in processes, documentation, and reporting, reducing ambiguity and enhancing operational transparency.
4. Enhancing Organizational Accountability
By assigning compliance responsibilities to teams and individuals, a CMS fosters a culture of accountability. It ensures employees are aware of compliance requirements and trained to uphold ethical and legal standards.
5. Improving Risk Management and Decision-Making
With real-time compliance tracking and data-driven insights, organizations can make informed decisions. A CMS helps businesses proactively address compliance gaps, preventing costly legal and operational disruptions.
6. Streamlining Audits and Reporting
A CMS simplifies internal and external audits by maintaining comprehensive records of compliance activities. Automated reporting features ensure timely submissions, reducing administrative burdens and improving regulatory transparency.
Examples of Compliance Management Systems
Different industries rely on various compliance management systems tailored to their regulatory requirements. Below are some common examples of CMS platforms and frameworks used across sectors:
1. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) RMF is widely used in cybersecurity and IT governance. It provides a structured approach to risk assessment, security controls, and compliance with federal regulations like FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act).
2. ISO 37301 – Compliance Management System Standard
The ISO 37301 standard offers a globally recognized framework for designing, implementing, and maintaining compliance management systems. It helps organizations establish best practices for regulatory adherence and risk mitigation.
3. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Software
Many organizations use GRC platforms like SAP GRC, MetricStream, and RSA Archer to automate compliance processes. These tools assist in policy management, risk assessments, and regulatory reporting.
4. Financial Compliance Systems
Banks and financial institutions rely on compliance solutions like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) software to meet regulatory requirements. Platforms such as FIS, Actimize, and Amlock help monitor transactions for suspicious activities.
5. HIPAA Compliance Management (Healthcare)
In healthcare, compliance management systems ensure adherence to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Platforms like Compliancy Group and Accountable help healthcare providers safeguard patient data and meet privacy regulations.
6. Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance Systems
Industries like manufacturing and energy use EHS compliance systems (e.g., Intelex, Enablon, and VelocityEHS) to manage workplace safety, environmental regulations, and sustainability initiatives.
A well-implemented compliance management system enables organizations to navigate complex regulations efficiently, reducing risk while fostering operational excellence. Choosing the right CMS depends on industry requirements, regulatory mandates, and organizational needs.
Key Elements of a Compliance Management System
A comprehensive Compliance Management System comprises several key elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring effective regulatory adherence. These elements can be broadly categorized as:

Policy Management:
- Establishing and communicating policies and procedures to relevant stakeholders, to ensure alignment with regulatory requirements.
- Periodic reviews and updates to accommodate changes in external regulations or internal processes.
Risk Assessment:
- Identifying and assessing potential compliance risks associated with business operations.
- Prioritizing risks based on severity and likelihood, enabling a focused mitigation strategy.
Incident Management:
- Establishing a system to track and manage compliance incidents promptly.
- Measuring the tangible and intangible costs of non-compliance.
- Implementing corrective actions to prevent future occurrences.
Training and Communication:
- Providing ongoing training to employees on compliance policies and procedures.
- Facilitating transparent communication channels for reporting potential compliance issues.
Monitoring and Auditing:
- Regularly monitoring and auditing business processes to ensure compliance.
- Conducting internal and external audits to validate the effectiveness of the CMS.
The Benefits of Using a Compliance Management System
Implementing a robust Compliance Management System yields a plethora of benefits for organizations navigating the intricate web of regulations. Some of the key advantages include:
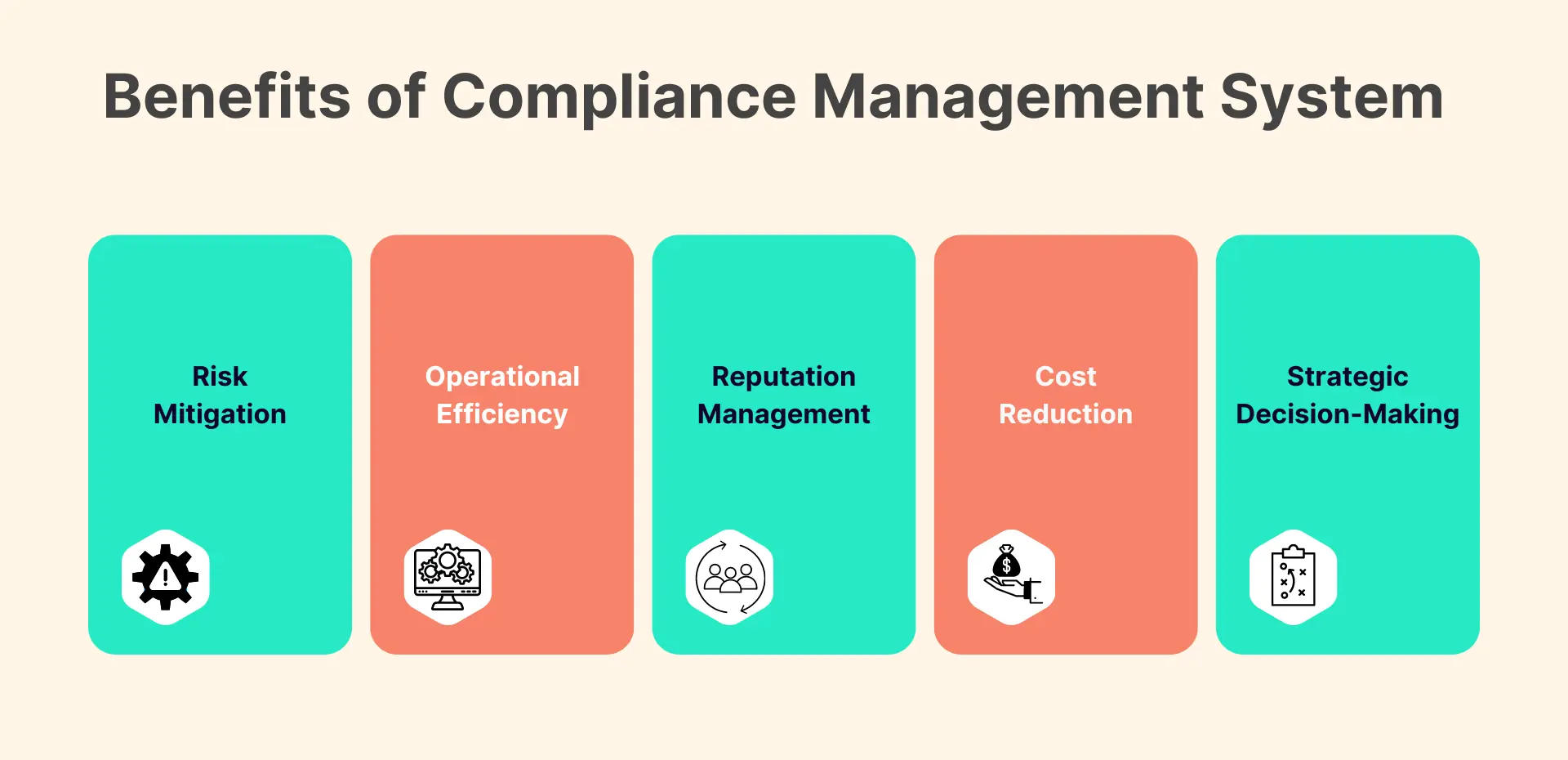
Risk Mitigation:
Proactively identifying and mitigating compliance risks reduces the likelihood of legal and financial repercussions. The idea behind using a Compliance Management System here is to reduce dependency on manual input, or distributed responsibility that inevitably arises when multiple stakeholders own the risk function.
Operational Efficiency:
A Compliance Management System (CMS) enhances operational efficiency by centralizing compliance-related information, automating workflows, and providing real-time monitoring.
It streamlines risk management, facilitates transparent communication, and enables data-driven decision-making. By optimizing compliance processes, a CMS ensures consistent adherence to regulations, minimizes the risk of errors, and allows organizations to allocate resources strategically for their core business activities.Reputation Management:
Ensuring compliance fosters trust among stakeholders, safeguarding an organization's reputation in the market. Trust in this context is a direct consequence of the availability of structured information and records maintained according to acceptable standards- a process that a good CMS effectively executes.
Cost Reduction:
Preventing compliance incidents and associated fines contributes to cost reduction and financial stability. Over the longer-term, this benefit also translates into lower risk exposure for the organization.
Strategic Decision-Making:
Access to real-time compliance data empowers leaders to make informed, strategic decisions in alignment with regulatory requirements.
How to Choose the Best Compliance Management System in 2025
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of compliance management solutions continues to evolve, but complex and complicated are two vastly different things. Often, what deters enterprises from implementing a CMS is the fear of a bad implementation. The way to ensure a successful implementation is to consider these five aspects before going ahead with a Compliance Management Solution:
- Scalability: Ensure the CMS can scale with the growth of your organization, accommodating an increasing volume of data and compliance requirements. Indeed, lack of effective scalability is a challenge that haunts many CMSs and their implementing organizations. Scale in this context refers not only to the vast swathes of data that need to be handled, but the diversity of data points that need to be collected as an organization grows.
- Integration Capabilities: Select a CMS that seamlessly integrates with existing enterprise systems, fostering a cohesive and interconnected GRC ecosystem.
- User-Friendly Interface: A user-friendly interface is paramount for widespread adoption within the organization. Look for intuitive design and easy navigation. Dig deeper with intuitive features and alert systems customized by job roles and functions. MetricStream’s Compliance Management Solution is powered with enhanced visual reporting to help leaders spend less time on reports and more on action.
- Automation and AI Capabilities: Leverage the power of automation and artificial intelligence for efficient data analysis, risk assessment, and incident management. Harness the capabilities of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to swiftly pinpoint issues by analyzing relationships, criticality, and business impact, providing insightful recommendations for issue classification. Develop and execute remediation plans, direct them to reviewers for approval, and facilitate real-time tracking of the entire issue remediation process. Utilize AI/ML to expedite these tasks, ensuring a streamlined and efficient approach to issue identification and resolution.
- Regulatory Intelligence: Capture, store, and oversee regulations by integrating the product software with trustworthy and authoritative regulatory content sources. Align regulatory updates with risks, controls, and policies, and stay abreast of these changes with automated notifications and alerts, ensuring timely and informed responses to evolving regulatory landscapes.
How to Set Up a Compliance Management System
Setting up a compliance management system ensures that an organization adheres to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards while effectively managing compliance risks. A well-structured CMS helps businesses maintain operational integrity, avoid penalties, and streamline compliance processes. Below are the key steps to establish an effective CMS:
1. Define Compliance Objectives and Scope
Start by identifying the compliance requirements relevant to your industry, including legal regulations, industry standards, and internal policies. Determine the scope of your CMS by outlining the specific areas of compliance your organization needs to address, such as data privacy, financial regulations, workplace safety, or environmental standards.
2. Establish Compliance Policies and Procedures
Develop clear and comprehensive compliance policies and procedures that align with regulatory requirements. These policies should outline:
- Code of conduct and ethical guidelines
- Roles and responsibilities of employees and management
- Procedures for reporting and handling compliance violations
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
3. Appoint a Compliance Team or Officer
Assign a compliance officer or team responsible for implementing and overseeing compliance activities. This team should be well-versed in industry regulations and able to ensure company-wide adherence to compliance policies.
4. Conduct a Risk Assessment
Identify potential compliance risks by evaluating business operations, third-party interactions, and regulatory obligations. Use risk assessment frameworks such as ISO 31000 or NIST RMF to categorize risks based on likelihood and impact, allowing for targeted mitigation efforts.
5. Implement Compliance Controls and Procedures
Develop and enforce internal controls, workflows, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance. This may include:
- Automated compliance tracking tools
- Employee access controls and data security measures
- Financial auditing systems
- Incident response protocols
6. Provide Compliance Training and Awareness
Regular training sessions ensure employees understand compliance policies and their responsibilities. Use a mix of workshops, e-learning modules, and case studies to keep staff informed about evolving regulations and best practices.
7. Establish Monitoring and Auditing Mechanisms
Implement continuous monitoring, auditing, and reporting processes to track compliance performance. Regular internal audits help identify gaps, prevent violations, and ensure compliance standards are being met. Use compliance management software to automate monitoring and generate reports.
8. Develop a Reporting and Incident Response System
Set up a whistleblower program or an anonymous reporting system where employees can report non-compliance issues without fear of retaliation. Have a clear incident response plan to investigate, address, and rectify compliance breaches promptly.
9. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes
Regulatory landscapes evolve, making it crucial to stay informed about legal updates and industry regulations. Subscribe to compliance newsletters, engage with industry associations, and regularly review policies to ensure ongoing compliance.
10. Continuously Improve the Compliance Program
Compliance management is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation, adaptation, and enhancement. Conduct regular assessments, collect feedback, and update policies to align with new risks, regulations, and business needs.
Setting up a compliance management system requires a structured approach that integrates policies, risk assessments, training, and monitoring. By implementing a well-defined CMS, organizations can mitigate risks, maintain regulatory adherence, and foster a culture of compliance, ensuring long-term success and operational integrity.
Conclusion
In the intricate dance between regulations, risks, and governance, Compliance Management Systems emerge as the silent guardians of organizational integrity. As enterprises grapple with the ever-expanding labyrinth of compliance requirements, a well-implemented CMS becomes not just a tool but a strategic asset. The benefits are manifold, ranging from risk mitigation and operational efficiency to reputation management and cost reduction.
The decision to invest in a Compliance Management System is not just a technological one; it is a strategic imperative for any organization aspiring to navigate the complex seas of regulatory compliance successfully. As we stand on the cusp of 2025, the quest for the ideal CMS becomes more crucial than ever. By aligning with the right compliance management solution, organizations can not only weather the storm of regulations but also set sail towards a future of sustainable growth and resilience in the face of an ever-changing business landscape.
In the not-so-distant past, giants of the industry have found themselves entangled in the web of regulatory missteps. The fallout was swift and unforgiving. Financial institutions, once pillars of stability, stumbled as regulatory oversights led to colossal fines and tarnished reputations, and the Lehman Brothers fiasco still rings fresh in our minds.
Consider the tech juggernauts, once soaring on the wings of innovation. In the wake of compliance lapses, their meteoric rise faced abrupt interruptions as legal battles and public scrutiny cast shadows over their technological prowess. All of this might make compliance seem like an arduous task, when in fact it could help stop these very mishaps from taking place. The reverberations of these real-world examples serve as cautionary tales, underscoring the paramount importance of Compliance Management Systems in the modern enterprise.
A compliance management system (CMS) is a structured framework that enables organizations to adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical requirements by implementing policies, procedures, and controls. It helps identify, assess, and mitigate compliance risks while ensuring operational integrity. In a dynamic regulatory environment, a CMS simplifies compliance efforts, enhances accountability, and minimizes the risks of non-compliance.
In the ever-evolving regulatory landscape, enterprises grapple with an increasing number of rules and standards. A CMS acts as a centralized hub, streamlining compliance efforts and mitigating the complexities associated with regulatory adherence.
The need for a robust Compliance Management System transcends industry boundaries, as organizations of all sizes grapple with the growing intricacies of compliance. In the GRC space, the focus is on enterprises that are subject to a multitude of regulations, standards, and internal policies. This includes but is not limited to financial institutions, healthcare providers, energy companies, and those in the technology sector.
Experts at MetricStream unanimously agree that organizations that fit into one or more of these criteria should consider investing in a compliance management system.
- Organizations that are subject to greater regulatory scrutiny either by virtue of their industry of operation (such as BFSI), or due to milestone events such as going public.
- Organizations with large and diverse teams spread across geographies, and having internal structures that are different among teams.
- Companies where compliance or lack thereof has led to significant issues in the past, either due to a lack of awareness, or due to oversight from some teams.
A compliance management system (CMS) plays a crucial role in helping organizations adhere to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards while minimizing risks. It provides a structured approach to compliance, ensuring that businesses operate within established guidelines and avoid penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Below are the key purposes of a CMS:
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
A CMS helps organizations stay compliant with industry-specific laws, governmental regulations, and international standards. It monitors updates in legal requirements and ensures policies and processes align with changing compliance landscapes.
2. Mitigating Compliance Risks
Non-compliance can lead to financial losses, legal actions, and reputational harm. A CMS identifies, assesses, and mitigates compliance risks by implementing controls, automating monitoring, and ensuring adherence to protocols.
3. Standardizing Policies and Procedures
Organizations operate more efficiently when they have well-defined compliance policies. A CMS ensures consistency in processes, documentation, and reporting, reducing ambiguity and enhancing operational transparency.
4. Enhancing Organizational Accountability
By assigning compliance responsibilities to teams and individuals, a CMS fosters a culture of accountability. It ensures employees are aware of compliance requirements and trained to uphold ethical and legal standards.
5. Improving Risk Management and Decision-Making
With real-time compliance tracking and data-driven insights, organizations can make informed decisions. A CMS helps businesses proactively address compliance gaps, preventing costly legal and operational disruptions.
6. Streamlining Audits and Reporting
A CMS simplifies internal and external audits by maintaining comprehensive records of compliance activities. Automated reporting features ensure timely submissions, reducing administrative burdens and improving regulatory transparency.
Different industries rely on various compliance management systems tailored to their regulatory requirements. Below are some common examples of CMS platforms and frameworks used across sectors:
1. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) RMF is widely used in cybersecurity and IT governance. It provides a structured approach to risk assessment, security controls, and compliance with federal regulations like FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act).
2. ISO 37301 – Compliance Management System Standard
The ISO 37301 standard offers a globally recognized framework for designing, implementing, and maintaining compliance management systems. It helps organizations establish best practices for regulatory adherence and risk mitigation.
3. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Software
Many organizations use GRC platforms like SAP GRC, MetricStream, and RSA Archer to automate compliance processes. These tools assist in policy management, risk assessments, and regulatory reporting.
4. Financial Compliance Systems
Banks and financial institutions rely on compliance solutions like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) software to meet regulatory requirements. Platforms such as FIS, Actimize, and Amlock help monitor transactions for suspicious activities.
5. HIPAA Compliance Management (Healthcare)
In healthcare, compliance management systems ensure adherence to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Platforms like Compliancy Group and Accountable help healthcare providers safeguard patient data and meet privacy regulations.
6. Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance Systems
Industries like manufacturing and energy use EHS compliance systems (e.g., Intelex, Enablon, and VelocityEHS) to manage workplace safety, environmental regulations, and sustainability initiatives.
A well-implemented compliance management system enables organizations to navigate complex regulations efficiently, reducing risk while fostering operational excellence. Choosing the right CMS depends on industry requirements, regulatory mandates, and organizational needs.
A comprehensive Compliance Management System comprises several key elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring effective regulatory adherence. These elements can be broadly categorized as:

Policy Management:
- Establishing and communicating policies and procedures to relevant stakeholders, to ensure alignment with regulatory requirements.
- Periodic reviews and updates to accommodate changes in external regulations or internal processes.
Risk Assessment:
- Identifying and assessing potential compliance risks associated with business operations.
- Prioritizing risks based on severity and likelihood, enabling a focused mitigation strategy.
Incident Management:
- Establishing a system to track and manage compliance incidents promptly.
- Measuring the tangible and intangible costs of non-compliance.
- Implementing corrective actions to prevent future occurrences.
Training and Communication:
- Providing ongoing training to employees on compliance policies and procedures.
- Facilitating transparent communication channels for reporting potential compliance issues.
Monitoring and Auditing:
- Regularly monitoring and auditing business processes to ensure compliance.
- Conducting internal and external audits to validate the effectiveness of the CMS.
Implementing a robust Compliance Management System yields a plethora of benefits for organizations navigating the intricate web of regulations. Some of the key advantages include:

Risk Mitigation:
Proactively identifying and mitigating compliance risks reduces the likelihood of legal and financial repercussions. The idea behind using a Compliance Management System here is to reduce dependency on manual input, or distributed responsibility that inevitably arises when multiple stakeholders own the risk function.
Operational Efficiency:
A Compliance Management System (CMS) enhances operational efficiency by centralizing compliance-related information, automating workflows, and providing real-time monitoring.
It streamlines risk management, facilitates transparent communication, and enables data-driven decision-making. By optimizing compliance processes, a CMS ensures consistent adherence to regulations, minimizes the risk of errors, and allows organizations to allocate resources strategically for their core business activities.Reputation Management:
Ensuring compliance fosters trust among stakeholders, safeguarding an organization's reputation in the market. Trust in this context is a direct consequence of the availability of structured information and records maintained according to acceptable standards- a process that a good CMS effectively executes.
Cost Reduction:
Preventing compliance incidents and associated fines contributes to cost reduction and financial stability. Over the longer-term, this benefit also translates into lower risk exposure for the organization.
Strategic Decision-Making:
Access to real-time compliance data empowers leaders to make informed, strategic decisions in alignment with regulatory requirements.
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of compliance management solutions continues to evolve, but complex and complicated are two vastly different things. Often, what deters enterprises from implementing a CMS is the fear of a bad implementation. The way to ensure a successful implementation is to consider these five aspects before going ahead with a Compliance Management Solution:
- Scalability: Ensure the CMS can scale with the growth of your organization, accommodating an increasing volume of data and compliance requirements. Indeed, lack of effective scalability is a challenge that haunts many CMSs and their implementing organizations. Scale in this context refers not only to the vast swathes of data that need to be handled, but the diversity of data points that need to be collected as an organization grows.
- Integration Capabilities: Select a CMS that seamlessly integrates with existing enterprise systems, fostering a cohesive and interconnected GRC ecosystem.
- User-Friendly Interface: A user-friendly interface is paramount for widespread adoption within the organization. Look for intuitive design and easy navigation. Dig deeper with intuitive features and alert systems customized by job roles and functions. MetricStream’s Compliance Management Solution is powered with enhanced visual reporting to help leaders spend less time on reports and more on action.
- Automation and AI Capabilities: Leverage the power of automation and artificial intelligence for efficient data analysis, risk assessment, and incident management. Harness the capabilities of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to swiftly pinpoint issues by analyzing relationships, criticality, and business impact, providing insightful recommendations for issue classification. Develop and execute remediation plans, direct them to reviewers for approval, and facilitate real-time tracking of the entire issue remediation process. Utilize AI/ML to expedite these tasks, ensuring a streamlined and efficient approach to issue identification and resolution.
- Regulatory Intelligence: Capture, store, and oversee regulations by integrating the product software with trustworthy and authoritative regulatory content sources. Align regulatory updates with risks, controls, and policies, and stay abreast of these changes with automated notifications and alerts, ensuring timely and informed responses to evolving regulatory landscapes.
Setting up a compliance management system ensures that an organization adheres to legal, regulatory, and ethical standards while effectively managing compliance risks. A well-structured CMS helps businesses maintain operational integrity, avoid penalties, and streamline compliance processes. Below are the key steps to establish an effective CMS:
1. Define Compliance Objectives and Scope
Start by identifying the compliance requirements relevant to your industry, including legal regulations, industry standards, and internal policies. Determine the scope of your CMS by outlining the specific areas of compliance your organization needs to address, such as data privacy, financial regulations, workplace safety, or environmental standards.
2. Establish Compliance Policies and Procedures
Develop clear and comprehensive compliance policies and procedures that align with regulatory requirements. These policies should outline:
- Code of conduct and ethical guidelines
- Roles and responsibilities of employees and management
- Procedures for reporting and handling compliance violations
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
3. Appoint a Compliance Team or Officer
Assign a compliance officer or team responsible for implementing and overseeing compliance activities. This team should be well-versed in industry regulations and able to ensure company-wide adherence to compliance policies.
4. Conduct a Risk Assessment
Identify potential compliance risks by evaluating business operations, third-party interactions, and regulatory obligations. Use risk assessment frameworks such as ISO 31000 or NIST RMF to categorize risks based on likelihood and impact, allowing for targeted mitigation efforts.
5. Implement Compliance Controls and Procedures
Develop and enforce internal controls, workflows, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance. This may include:
- Automated compliance tracking tools
- Employee access controls and data security measures
- Financial auditing systems
- Incident response protocols
6. Provide Compliance Training and Awareness
Regular training sessions ensure employees understand compliance policies and their responsibilities. Use a mix of workshops, e-learning modules, and case studies to keep staff informed about evolving regulations and best practices.
7. Establish Monitoring and Auditing Mechanisms
Implement continuous monitoring, auditing, and reporting processes to track compliance performance. Regular internal audits help identify gaps, prevent violations, and ensure compliance standards are being met. Use compliance management software to automate monitoring and generate reports.
8. Develop a Reporting and Incident Response System
Set up a whistleblower program or an anonymous reporting system where employees can report non-compliance issues without fear of retaliation. Have a clear incident response plan to investigate, address, and rectify compliance breaches promptly.
9. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes
Regulatory landscapes evolve, making it crucial to stay informed about legal updates and industry regulations. Subscribe to compliance newsletters, engage with industry associations, and regularly review policies to ensure ongoing compliance.
10. Continuously Improve the Compliance Program
Compliance management is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation, adaptation, and enhancement. Conduct regular assessments, collect feedback, and update policies to align with new risks, regulations, and business needs.
Setting up a compliance management system requires a structured approach that integrates policies, risk assessments, training, and monitoring. By implementing a well-defined CMS, organizations can mitigate risks, maintain regulatory adherence, and foster a culture of compliance, ensuring long-term success and operational integrity.
In the intricate dance between regulations, risks, and governance, Compliance Management Systems emerge as the silent guardians of organizational integrity. As enterprises grapple with the ever-expanding labyrinth of compliance requirements, a well-implemented CMS becomes not just a tool but a strategic asset. The benefits are manifold, ranging from risk mitigation and operational efficiency to reputation management and cost reduction.
The decision to invest in a Compliance Management System is not just a technological one; it is a strategic imperative for any organization aspiring to navigate the complex seas of regulatory compliance successfully. As we stand on the cusp of 2025, the quest for the ideal CMS becomes more crucial than ever. By aligning with the right compliance management solution, organizations can not only weather the storm of regulations but also set sail towards a future of sustainable growth and resilience in the face of an ever-changing business landscape.








