Introduction
We live in turbulent times with health challenges, war, volatile economic conditions, and an escalating climate crisis disrupting business and life. For the corporate world, this increased global volatility brings increased risks, necessitating constant vigilance, and countermeasures. More so, with the interconnectedness of cyber, geopolitical, third-party, physical, privacy, financial, and ESG risks, to name a few.
Instituting a Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) strategy is the most efficient way when it comes to managing modern-day risks that are complex, interconnected, and constantly evolving.
This article aims to unravel the complexities of GRC offering insights into best practices, emerging trends and the integration of technology in shaping a robust GRC strategy that your organization can use to navigate the complexities of the modern business environment with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a comprehensive way to approach risks, which helps organizations comply with regulations while aligning day-to-day operations with strategic goals.
- Implementing GRC can help organizations improve visibility and transparency, enhance their risk management, improve their compliance, create better alignment with business goals, foster improved communication and collaboration, and promote good governance.
- By following specific policies and processes related to governance, risk, and compliance, organizations can manage all three components effectively, leading to more standardized, efficient, and compliant outcomes.
- GRC maturity is a way to determine an organization's level of sophistication and effectiveness in implementing and managing its governance, risk management, and compliance programs. It is usually assessed through certain criteria that determine how effectively each of the steps are being followed.
- Asking the right questions before making a decision can ensure you select a GRC tool that best aligns with your unique requirements and goals.
- Implementing GRC effectively comes with a number of challenges, but following a step-by-step process can help ease the transition.
What is GRC?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a holistic approach to managing an organization's risks, ensuring compliance with regulations, and aligning operations with strategic goals. Implementing a comprehensive GRC program helps improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance business performance and growth.
GRC encompasses tools and software solutions that help an organization manage risk management, compliance, and governance activities with an integrated approach.
According to OCEG, GRC is defined as “the integrated collection of capabilities that enable an organization to reliably achieve objectives, address uncertainty, and act with integrity.”
What Does GRC include?

- Governance: Think of it as the compass guiding your organization's ethical and transparent operations. It ensures decisions align with your strategic goals and values.
- Risk Management: This is your safety net, identifying and mitigating potential threats before they derail your progress and strategically using risks to your advantage.
- Compliance: It's playing by the rules, adhering to relevant laws and industry standards to maintain trust and avoid costly penalties.
What is a GRC Model?
A GRC model is a foundational framework that outlines and integrates the key components and processes involved in Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC). GRC models often leverage various software solutions and tools to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and improve data analysis.
A comprehensive GRC program includes two elements:
GRC requirements are standard components of a strong GRC strategy that combine internal and external factors into a comprehensive framework to achieve effective governance, robust risk management, and consistent compliance.
- An integrated and connected strategy that helps organizations manage governance, risks, and compliance with industry standards
- The tools and processes used to centralize, manage, and deploy a company-wide GRC solution

What is the Importance of GRC?
In today's complex business landscape, GRC has become a fundamental necessity for organizations of all sizes and across all industries. By embracing a connected GRC approach, your organization can unlock a treasure trove of benefits, including:
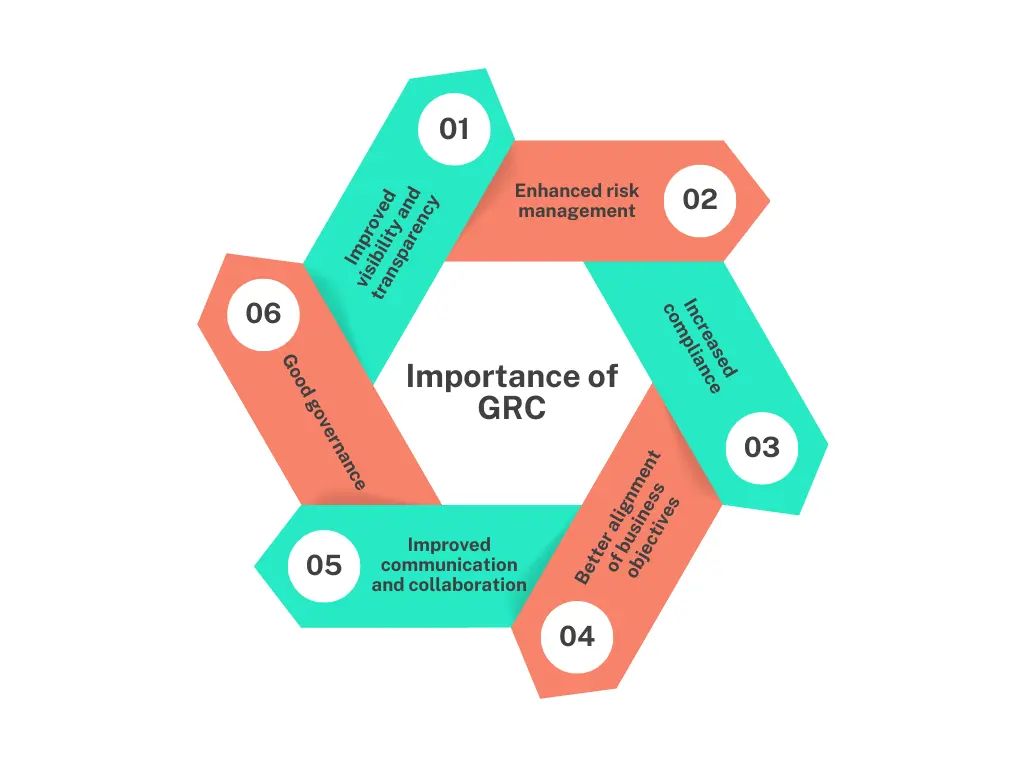
Improved visibility and transparency
With a holistic view of an organization's governance, risk, and compliance practices, your organization can now make better decisions and ensure transparency and accountability.
Enhanced risk management
By being able to identify and assess risks, implement controls to mitigate them, and monitor their effectiveness your organization gains better risk management practices and reduces the likelihood of potential crises.
Increased compliance
GRC ensures that an organization complies with applicable laws, regulations, and standards. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties, reputational damage, and legal disputes for your organization.
Better alignment of business objectives
By aligning business objectives with governance, risk management, and compliance practices, you can ensure more effective and efficient business operations and enhanced stakeholder trust.
Improved communication and collaboration
GRC provides a common language and framework for various departments and functions within an organization, facilitating better communication and collaboration. This results in more efficient and effective decision-making.
Good governance
Overall, GRC enables organizations to achieve good governance by promoting transparency, accountability, risk management, compliance, and stakeholder trust.
GRC Use Cases
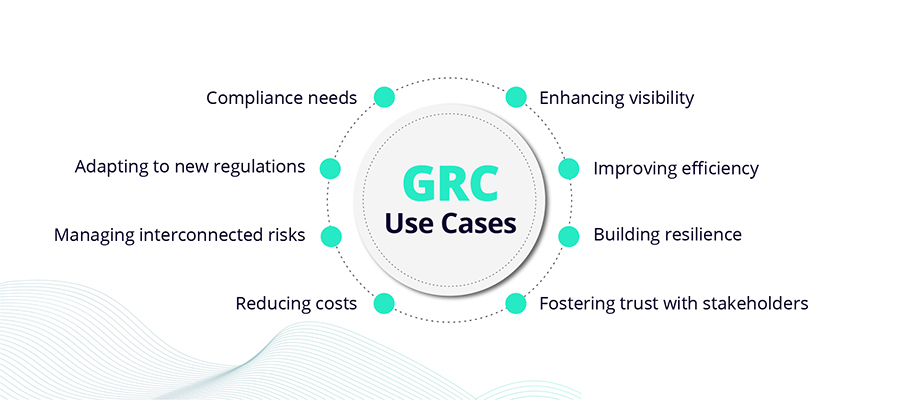
Although most organizations have initiatives designed to improve internal controls, corporate governance, and risk management, they continue to face challenges. Listed below are a few reasons why organizations are increasingly seeking more effective GRC systems. :
- The need for effective compliance with laws, regulations, and standards applicable to the organization's operations and industry.
- An increasing number of new and updated regulations require a robust GRC program to prepare for emerging regulations and to seamlessly adapt and absorb to changing requirements
- An increasingly interconnected risk landscape, where a cyber risk or ESG risk in your supply chain requires more than a conventional vendor or third-party risk management
- Managing the rising costs of compliance and risk management when approached in a siloed and disconnected manner
- The requirement for greater visibility into the organization's activities and communication with stakeholders
- A need to improve operational efficiency and effectiveness by streamlining processes and eliminating duplication
- To be able to build business resilience and gain the agility to prepare for and respond to crises or unexpected events that could impact the organization's operations, reputation, or financial performance
- To effectively build trust and confidence with stakeholders, including customers, shareholders, employees, regulators, and other third parties.
How Does GRC Work?
GRC works by bringing the three foundational components - Governance, Risk management, and Compliance – together via an integrated and connected approach. These components work in tandem to ensure that an organization operates effectively, manages risks efficiently, and adheres to all relevant regulations.
To explain further, GRC works in three key movements:
- Setting the Score: Clear governance policies and procedures establish the foundation, guiding ethical decision-making and aligning operations with strategic goals. Think of it as defining the musical piece the organization will perform.
- Anticipating Discord: Proactive risk assessments identify potential threats like cyberattacks or data breaches, allowing for mitigation strategies to be implemented before they disrupt performance. This is like the conductor identifying potential off-key notes and adjusting accordingly.
Playing by the Rules: By adhering to relevant laws and industry standards, GRC ensures the organization stays compliant and avoids costly penalties. It's like following the sheet music to ensure the performance stays within the boundaries of regulations.
GRC Capabilities
GRC capabilities are the building blocks that enable organizations to implement a successful GRC program. These capabilities encompass a wide range of tools, processes, and practices that work together to achieve principled performance. This means reliably achieving objectives, addressing uncertainty, and acting with integrity.
Here's a breakdown of some key GRC capabilities
Governance Risk Management Compliance Corporate management, which includes how relationships within the organization are structured and the organization’s hierarchy. The identification of existing and potential risks that an organization faces. Alignment and best practices around applicable regulations, conduct rules, and expectations Mapping the organization’s goals with individual responsibility and accountability. Risk assessment, wherein all assets and risks are inventoried and assessed for potential gaps. A means for an organization to pursue demonstrable integrity, trust, and legal compliance Policy management for everyday activities. As organizations grow, standardizing everyday processes is one way to ensure smooth operations. Managing risks by classifying them based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential business impact. As an extension, risks that are more likely and have a larger business impact can be prioritized for faster mitigation. Internal and external auditing and controls to comply with set standards Implementing security measures and protocols Reporting tools, metrics, and formats that ensure clean records for both internal and external compliance.
What is GRC Maturity?
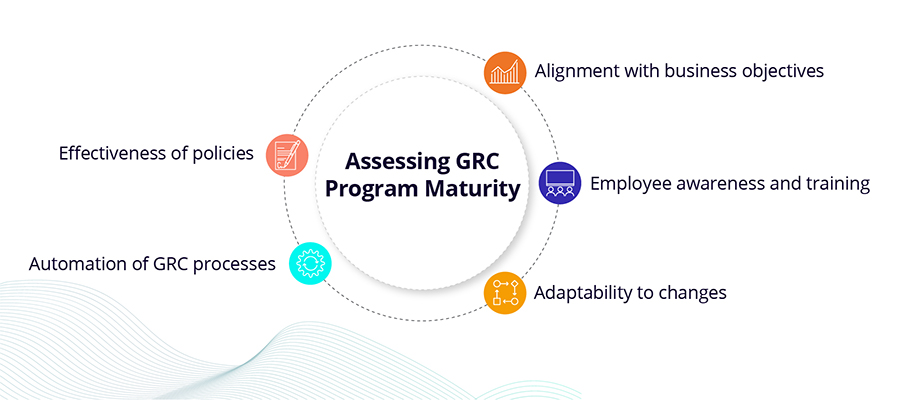
GRC maturity refers to an organization's level of sophistication and effectiveness in implementing and managing its governance, risk management, and compliance programs. The maturity of an organization's GRC program can be assessed through various criteria, such as:
- the effectiveness of its policies
- the level of automation of its GRC processes
- the alignment of its GRC program with its business objectives
- the awareness and training of its employees
- the organization's ability to monitor and adapt to changes in its GRC environment
An organization with a high level of GRC maturity typically has a well-defined GRC program that is integrated into its overall business strategy and operations. It also has a proactive and agile approach to risk management, compliance, and governance that enables it to identify, assess, and respond to risks and compliance issues effectively. In contrast, an organization with a low level of GRC maturity may have an ad-hoc and reactive approach to GRC, which can lead to inefficient processes, inadequate risk management, and compliance failures.
Assessing an organization's GRC maturity can help it identify areas of improvement and develop a roadmap for enhancing its GRC program over time.
How to Assess GRC Maturity?
GRC maturity can be assessed through various methods, including maturity models, benchmarking against industry standards, and conducting internal assessments.
Here are key steps to help you access your organization's GRC maturity:
Step 1: Identify your organization's GRC framework and processes
Determine the processes and frameworks your organization has in place to manage governance, risk, and compliance activities. This will help you assess the current state of your organization's GRC maturity.
Step 2: Assess the effectiveness of your organization's GRC processes
Conduct an evaluation of your organization's GRC processes to determine their effectiveness. You can use various methods, including surveys, interviews, and audits.
Step 3: Use a GRC maturity model
A GRC maturity model can help you assess your organization's GRC maturity level. You can use a standard model or develop one specific to your organization's needs.
Step 4: Benchmark against industry standards
Compare your organization's GRC maturity level against industry standards and best practices. This will help you determine how your organization stacks up against its peers.
Step 5: Develop a roadmap
Based on your assessment, create a roadmap for improving your organization's GRC maturity level. This should include specific actions and timelines for implementation.
Step 6: Monitor and evaluate progress
Regularly monitor and evaluate your organization's progress towards improving its GRC maturity level. This will help you determine if you are on track to achieving your goals and identify areas where further improvements are needed.
How to Choose the Right GRC Software Solution?
Asking the right questions before making a decision can ensure you select a GRC tool that best aligns with your unique requirements and goals. Here are some key questions to consider:
- Does it do what it’s supposed to do?
- Am I able to effectively identify, prioritize, mitigate, and reduce my risk with this GRC solution?
- Is the GRC software built to scale
- Are there integrations available? Can it work in conjunction with SharePoint, can it deliver reporting through a BI tool, can it integrate with an existing component of another GRC solution, delivering a more holistic experience?
- Are others in my industry using this software solution successfully?
- Can I assess my risks and mitigation plans and activities easily and comprehensively, and can I easily share reporting and analytics with my bosses and the board?
- With that kind of visibility into my GRC program and its performance, can I refocus my energies away from worry about GRC / risks and on to more strategic and performance-oriented tasks and tactics?
- Does it allow me to be more strategic, productive, and confident in my job?
- Does the GRC software scale. and is it flexible enough to handle unforeseen changes in the business?
- What happens if the business opens new operations or adds third-party engagements in different areas of the world?
- What new challenges would there be if the business gets acquired or merges with another business?
- Is it comprehensive enough to not need to be removed and replaced in the next five years, no matter what changes happen to the business or the risk and compliance environment?
- Does it offer me assurances that I am not buying something I will grow out of in a short time?
- Does it fit and is it customizable to my organization’s distinct needs, regulatory and risk environments?
- I live in a world where I depend on multiple software solutions and have an IT team investing in more. I can’t have a solution that requires constant IT configuration and reconfiguration to fit my needs. Does it allow for do-it-yourself adaptation?
- What is the vendor’s reputation? Is a vendor a conscientious partner, a good corporate citizen, and believes in fostering a culture of compassion, inclusion, and diversity?
Common GRC Tools
GRC tools are software applications designed to help organizations manage their compliance with regulations, policies, and standards, as well as identify and mitigate risks that could impact their operations. Some of the most common GRC tools include:
GRC Software for Compliance, Risk, Audit, and Vendor Management
These tools help organizations
- track and manage compliance requirements across multiple regulatory bodies and industry standards
- assist in identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to an organization and its assets
- manage audit process, including planning, scheduling, executing, and reporting on audits
- assist in managing incidents, including data breaches, security breaches, and compliance failures
- manage and track policies and procedures, including policy creation, revision, and distribution
- manage and monitor third-party vendors' compliance with regulatory requirements and contractual obligations
- assist in developing, implementing, and managing business continuity plans and strategies to ensure business operations can continue in the event of a disruption or disaster
GRC Software for IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance (IT GRC) and Cyber GRC
These tools help organizations:
- manage IT-related risks and compliance requirements, including data privacy and security regulations, and compliance with frameworks such as NIST, COSO, PCI-DSS, etc.
- streamline the creation and management of IT policies
- identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT vendor risks and manage vendor compliance
- simplify the identification, collation, prioritization, tracking, and remediation of cyber and information security threats and vulnerabilities
GRC Software for ESG
These tools help organizations:
- streamline all organizational requirements relating to Environmental, Social, Governance, Risk and Compliance (ESGRC), including managing ESG standards, frameworks, and disclosure requirements
Challenges in implementing GRC
Implementing a GRC framework comes with a few challenges, of which the key ones are:
1. Organizational Resistance: Employees or management could resist new technologies, or imply a significant financial strain, leading to low adoption. Another factor is the lack of awareness of the importance of GRC, or a lack of expertise in GRC frameworks, both of which can be a barrier to effective implementation.
2. Challenges with Processes and Technology: Depending on the number of departments handling the various components of GRC, the level of complexity in sharing information across teams can be a stumbling block. In addition, adding a new tool to a pre-existing system can be a challenge in itself. Certain tools may even carry their own risks, amplifying cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
3. Complexity of Regulations and Scope: While GRC frameworks can address a plethora of situations, identifying and implementing the specific portions of it that are relevant to the organization can be intimidating. Without a clear goal, or a specific set of regulatory requirements, businesses may suffer from a lack of clarity.
4. Difficulties in Documentation and Consistency: Defining KPIs, collecting relevant data, and creating the necessary documentation requires both effort and expertise, which can be difficult to manage. In addition, teams may view these tasks as a one-time process, when it actually requires continuous refining and reporting to be successful.
Addressing these challenges might call for a significant initial investment and an overall cultural shift within the organization, but with commitment from both leadership and the team, proper training, and regular audits, businesses can ensure that the framework evolves with organizational and regulatory changes.
How to implement GRC effectively
Adopting a phased approach to implementing GRC will ensure a structured and sustainable way to integrate GRC practices that are tailored to your organization’s needs.
1. Assess Current State and Define Objectives: Begin by comprehensively evaluating existing processes around governance, risk, and compliance to identify any gaps. Based on this, define the goals and objectives that need to be achieved. Ensure that these goals are aligned with the overall business strategy.
2. Gain Leadership Commitment and Build a Cross-Functional Team: Ensure leadership buy-in to help guide the process, manage funding, and gain visibility across teams. Next, a task force consisting of representatives from all key departments will be put together.
3. Develop a Unified GRC Framework: Select the right GRC framework for the organization based on its needs and industry. Standardize and document the various roles and processes needed to align governance, risk, and compliance activities.
4. Implement Technology Solutions: Invest in the right GRC tools that will help with both integration and automation. Next, consolidate all relevant data for complete visibility and analysis. Finally, integrate existing organizational systems with the chosen GRC solution.
5. Train Employees and Foster a Risk-Aware Culture: Ensure employees are trained on GRC principles and their role in its implementation and management. Encourage employees to take accountability and proactively identify and report issues.
6. Monitor, Audit, and Optimize: Define measurable metrics to track the success of implementation. Periodically review these metrics to ensure their effectiveness, and use feedback and audit reports to refine and modify GRC processes in an ongoing manner.
7. Communicate Progress to Stakeholders: Share both positive and negative outcomes with the relevant stakeholders to ensure transparency. Their input can also help with aligning the process to the organization’s needs and external requirements.
Why MetricStream BusinessGRC?
We, at MetricStream, understand the importance of an integrated and connected approach to bring together all three GRC elements - governance, risk, and compliance - to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving risk landscape.
MetricStream Business GRC enables organizations to adopt a holistic and connected approach to managing risks, regulatory requirements, audits, and third parties. Standardized GRC taxonomies and a consistent approach enable seamless collaboration across teams, simplifying the process of collecting and analyzing risk, compliance, audit, and third-party vendor data from across the enterprise for actionable insights. This provides an organization with a single source of truth and enables them to understand the interconnectedness of risks. Enriched with AI capabilities and advanced risk analytics, BusinessGRC is designed to help organizations keep up with the fast-changing risk and regulatory environment and improve their preparedness for unknown unknowns.
With MetricStream BusinessGRC, organizations can:
- Gain contextual risk and compliance information and predictive insights that can help strengthen the overall GRC posture.
- Accelerate decision-making through automated workflows and processes while reducing data redundancies and duplication of effort
- Create and maintain a gold source of data that drives effective firm-wide collaboration and coordination to identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
- Establish a robust and comprehensive foundation for good governance across the extended enterprise.
FAQ
What is the full form of GRC?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), and encompasses the tools and processes for identifying and managing risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and establishing good governance.
What is the difference between GRC and compliance?
GRC is an integrated approach to managing governance, risk, and compliance activities, while compliance is adhering to relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards.
What is the difference between GRC and ERM?
GRC refers to managing governance, risk, and compliance activities in a connected and coordinated manner, while ERM (enterprise risk management) is the process of identifying, assessing, managing and mitigating enterprise risks.
We live in turbulent times with health challenges, war, volatile economic conditions, and an escalating climate crisis disrupting business and life. For the corporate world, this increased global volatility brings increased risks, necessitating constant vigilance, and countermeasures. More so, with the interconnectedness of cyber, geopolitical, third-party, physical, privacy, financial, and ESG risks, to name a few.
Instituting a Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) strategy is the most efficient way when it comes to managing modern-day risks that are complex, interconnected, and constantly evolving.
This article aims to unravel the complexities of GRC offering insights into best practices, emerging trends and the integration of technology in shaping a robust GRC strategy that your organization can use to navigate the complexities of the modern business environment with confidence.
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a comprehensive way to approach risks, which helps organizations comply with regulations while aligning day-to-day operations with strategic goals.
- Implementing GRC can help organizations improve visibility and transparency, enhance their risk management, improve their compliance, create better alignment with business goals, foster improved communication and collaboration, and promote good governance.
- By following specific policies and processes related to governance, risk, and compliance, organizations can manage all three components effectively, leading to more standardized, efficient, and compliant outcomes.
- GRC maturity is a way to determine an organization's level of sophistication and effectiveness in implementing and managing its governance, risk management, and compliance programs. It is usually assessed through certain criteria that determine how effectively each of the steps are being followed.
- Asking the right questions before making a decision can ensure you select a GRC tool that best aligns with your unique requirements and goals.
- Implementing GRC effectively comes with a number of challenges, but following a step-by-step process can help ease the transition.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a holistic approach to managing an organization's risks, ensuring compliance with regulations, and aligning operations with strategic goals. Implementing a comprehensive GRC program helps improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance business performance and growth.
GRC encompasses tools and software solutions that help an organization manage risk management, compliance, and governance activities with an integrated approach.
According to OCEG, GRC is defined as “the integrated collection of capabilities that enable an organization to reliably achieve objectives, address uncertainty, and act with integrity.”
What Does GRC include?

- Governance: Think of it as the compass guiding your organization's ethical and transparent operations. It ensures decisions align with your strategic goals and values.
- Risk Management: This is your safety net, identifying and mitigating potential threats before they derail your progress and strategically using risks to your advantage.
- Compliance: It's playing by the rules, adhering to relevant laws and industry standards to maintain trust and avoid costly penalties.
What is a GRC Model?
A GRC model is a foundational framework that outlines and integrates the key components and processes involved in Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC). GRC models often leverage various software solutions and tools to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and improve data analysis.
A comprehensive GRC program includes two elements:
GRC requirements are standard components of a strong GRC strategy that combine internal and external factors into a comprehensive framework to achieve effective governance, robust risk management, and consistent compliance.
- An integrated and connected strategy that helps organizations manage governance, risks, and compliance with industry standards
- The tools and processes used to centralize, manage, and deploy a company-wide GRC solution

In today's complex business landscape, GRC has become a fundamental necessity for organizations of all sizes and across all industries. By embracing a connected GRC approach, your organization can unlock a treasure trove of benefits, including:

Improved visibility and transparency
With a holistic view of an organization's governance, risk, and compliance practices, your organization can now make better decisions and ensure transparency and accountability.
Enhanced risk management
By being able to identify and assess risks, implement controls to mitigate them, and monitor their effectiveness your organization gains better risk management practices and reduces the likelihood of potential crises.
Increased compliance
GRC ensures that an organization complies with applicable laws, regulations, and standards. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties, reputational damage, and legal disputes for your organization.
Better alignment of business objectives
By aligning business objectives with governance, risk management, and compliance practices, you can ensure more effective and efficient business operations and enhanced stakeholder trust.
Improved communication and collaboration
GRC provides a common language and framework for various departments and functions within an organization, facilitating better communication and collaboration. This results in more efficient and effective decision-making.
Good governance
Overall, GRC enables organizations to achieve good governance by promoting transparency, accountability, risk management, compliance, and stakeholder trust.

Although most organizations have initiatives designed to improve internal controls, corporate governance, and risk management, they continue to face challenges. Listed below are a few reasons why organizations are increasingly seeking more effective GRC systems. :
- The need for effective compliance with laws, regulations, and standards applicable to the organization's operations and industry.
- An increasing number of new and updated regulations require a robust GRC program to prepare for emerging regulations and to seamlessly adapt and absorb to changing requirements
- An increasingly interconnected risk landscape, where a cyber risk or ESG risk in your supply chain requires more than a conventional vendor or third-party risk management
- Managing the rising costs of compliance and risk management when approached in a siloed and disconnected manner
- The requirement for greater visibility into the organization's activities and communication with stakeholders
- A need to improve operational efficiency and effectiveness by streamlining processes and eliminating duplication
- To be able to build business resilience and gain the agility to prepare for and respond to crises or unexpected events that could impact the organization's operations, reputation, or financial performance
- To effectively build trust and confidence with stakeholders, including customers, shareholders, employees, regulators, and other third parties.
GRC works by bringing the three foundational components - Governance, Risk management, and Compliance – together via an integrated and connected approach. These components work in tandem to ensure that an organization operates effectively, manages risks efficiently, and adheres to all relevant regulations.
To explain further, GRC works in three key movements:
- Setting the Score: Clear governance policies and procedures establish the foundation, guiding ethical decision-making and aligning operations with strategic goals. Think of it as defining the musical piece the organization will perform.
- Anticipating Discord: Proactive risk assessments identify potential threats like cyberattacks or data breaches, allowing for mitigation strategies to be implemented before they disrupt performance. This is like the conductor identifying potential off-key notes and adjusting accordingly.
Playing by the Rules: By adhering to relevant laws and industry standards, GRC ensures the organization stays compliant and avoids costly penalties. It's like following the sheet music to ensure the performance stays within the boundaries of regulations.
GRC Capabilities
GRC capabilities are the building blocks that enable organizations to implement a successful GRC program. These capabilities encompass a wide range of tools, processes, and practices that work together to achieve principled performance. This means reliably achieving objectives, addressing uncertainty, and acting with integrity.
Here's a breakdown of some key GRC capabilities
Governance Risk Management Compliance Corporate management, which includes how relationships within the organization are structured and the organization’s hierarchy. The identification of existing and potential risks that an organization faces. Alignment and best practices around applicable regulations, conduct rules, and expectations Mapping the organization’s goals with individual responsibility and accountability. Risk assessment, wherein all assets and risks are inventoried and assessed for potential gaps. A means for an organization to pursue demonstrable integrity, trust, and legal compliance Policy management for everyday activities. As organizations grow, standardizing everyday processes is one way to ensure smooth operations. Managing risks by classifying them based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential business impact. As an extension, risks that are more likely and have a larger business impact can be prioritized for faster mitigation. Internal and external auditing and controls to comply with set standards Implementing security measures and protocols Reporting tools, metrics, and formats that ensure clean records for both internal and external compliance.
GRC maturity refers to an organization's level of sophistication and effectiveness in implementing and managing its governance, risk management, and compliance programs. The maturity of an organization's GRC program can be assessed through various criteria, such as:
- the effectiveness of its policies
- the level of automation of its GRC processes
- the alignment of its GRC program with its business objectives
- the awareness and training of its employees
- the organization's ability to monitor and adapt to changes in its GRC environment
An organization with a high level of GRC maturity typically has a well-defined GRC program that is integrated into its overall business strategy and operations. It also has a proactive and agile approach to risk management, compliance, and governance that enables it to identify, assess, and respond to risks and compliance issues effectively. In contrast, an organization with a low level of GRC maturity may have an ad-hoc and reactive approach to GRC, which can lead to inefficient processes, inadequate risk management, and compliance failures.
Assessing an organization's GRC maturity can help it identify areas of improvement and develop a roadmap for enhancing its GRC program over time.
How to Assess GRC Maturity?

GRC maturity can be assessed through various methods, including maturity models, benchmarking against industry standards, and conducting internal assessments.
Here are key steps to help you access your organization's GRC maturity:
Step 1: Identify your organization's GRC framework and processes
Determine the processes and frameworks your organization has in place to manage governance, risk, and compliance activities. This will help you assess the current state of your organization's GRC maturity.
Step 2: Assess the effectiveness of your organization's GRC processes
Conduct an evaluation of your organization's GRC processes to determine their effectiveness. You can use various methods, including surveys, interviews, and audits.
Step 3: Use a GRC maturity model
A GRC maturity model can help you assess your organization's GRC maturity level. You can use a standard model or develop one specific to your organization's needs.
Step 4: Benchmark against industry standards
Compare your organization's GRC maturity level against industry standards and best practices. This will help you determine how your organization stacks up against its peers.
Step 5: Develop a roadmap
Based on your assessment, create a roadmap for improving your organization's GRC maturity level. This should include specific actions and timelines for implementation.
Step 6: Monitor and evaluate progress
Regularly monitor and evaluate your organization's progress towards improving its GRC maturity level. This will help you determine if you are on track to achieving your goals and identify areas where further improvements are needed.
Asking the right questions before making a decision can ensure you select a GRC tool that best aligns with your unique requirements and goals. Here are some key questions to consider:
- Does it do what it’s supposed to do?
- Am I able to effectively identify, prioritize, mitigate, and reduce my risk with this GRC solution?
- Is the GRC software built to scale
- Are there integrations available? Can it work in conjunction with SharePoint, can it deliver reporting through a BI tool, can it integrate with an existing component of another GRC solution, delivering a more holistic experience?
- Are others in my industry using this software solution successfully?
- Can I assess my risks and mitigation plans and activities easily and comprehensively, and can I easily share reporting and analytics with my bosses and the board?
- With that kind of visibility into my GRC program and its performance, can I refocus my energies away from worry about GRC / risks and on to more strategic and performance-oriented tasks and tactics?
- Does it allow me to be more strategic, productive, and confident in my job?
- Does the GRC software scale. and is it flexible enough to handle unforeseen changes in the business?
- What happens if the business opens new operations or adds third-party engagements in different areas of the world?
- What new challenges would there be if the business gets acquired or merges with another business?
- Is it comprehensive enough to not need to be removed and replaced in the next five years, no matter what changes happen to the business or the risk and compliance environment?
- Does it offer me assurances that I am not buying something I will grow out of in a short time?
- Does it fit and is it customizable to my organization’s distinct needs, regulatory and risk environments?
- I live in a world where I depend on multiple software solutions and have an IT team investing in more. I can’t have a solution that requires constant IT configuration and reconfiguration to fit my needs. Does it allow for do-it-yourself adaptation?
- What is the vendor’s reputation? Is a vendor a conscientious partner, a good corporate citizen, and believes in fostering a culture of compassion, inclusion, and diversity?
GRC tools are software applications designed to help organizations manage their compliance with regulations, policies, and standards, as well as identify and mitigate risks that could impact their operations. Some of the most common GRC tools include:
GRC Software for Compliance, Risk, Audit, and Vendor Management
These tools help organizations
- track and manage compliance requirements across multiple regulatory bodies and industry standards
- assist in identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to an organization and its assets
- manage audit process, including planning, scheduling, executing, and reporting on audits
- assist in managing incidents, including data breaches, security breaches, and compliance failures
- manage and track policies and procedures, including policy creation, revision, and distribution
- manage and monitor third-party vendors' compliance with regulatory requirements and contractual obligations
- assist in developing, implementing, and managing business continuity plans and strategies to ensure business operations can continue in the event of a disruption or disaster
GRC Software for IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance (IT GRC) and Cyber GRC
These tools help organizations:
- manage IT-related risks and compliance requirements, including data privacy and security regulations, and compliance with frameworks such as NIST, COSO, PCI-DSS, etc.
- streamline the creation and management of IT policies
- identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT vendor risks and manage vendor compliance
- simplify the identification, collation, prioritization, tracking, and remediation of cyber and information security threats and vulnerabilities
GRC Software for ESG
These tools help organizations:
- streamline all organizational requirements relating to Environmental, Social, Governance, Risk and Compliance (ESGRC), including managing ESG standards, frameworks, and disclosure requirements
Implementing a GRC framework comes with a few challenges, of which the key ones are:
1. Organizational Resistance: Employees or management could resist new technologies, or imply a significant financial strain, leading to low adoption. Another factor is the lack of awareness of the importance of GRC, or a lack of expertise in GRC frameworks, both of which can be a barrier to effective implementation.
2. Challenges with Processes and Technology: Depending on the number of departments handling the various components of GRC, the level of complexity in sharing information across teams can be a stumbling block. In addition, adding a new tool to a pre-existing system can be a challenge in itself. Certain tools may even carry their own risks, amplifying cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
3. Complexity of Regulations and Scope: While GRC frameworks can address a plethora of situations, identifying and implementing the specific portions of it that are relevant to the organization can be intimidating. Without a clear goal, or a specific set of regulatory requirements, businesses may suffer from a lack of clarity.
4. Difficulties in Documentation and Consistency: Defining KPIs, collecting relevant data, and creating the necessary documentation requires both effort and expertise, which can be difficult to manage. In addition, teams may view these tasks as a one-time process, when it actually requires continuous refining and reporting to be successful.
Addressing these challenges might call for a significant initial investment and an overall cultural shift within the organization, but with commitment from both leadership and the team, proper training, and regular audits, businesses can ensure that the framework evolves with organizational and regulatory changes.
Adopting a phased approach to implementing GRC will ensure a structured and sustainable way to integrate GRC practices that are tailored to your organization’s needs.
1. Assess Current State and Define Objectives: Begin by comprehensively evaluating existing processes around governance, risk, and compliance to identify any gaps. Based on this, define the goals and objectives that need to be achieved. Ensure that these goals are aligned with the overall business strategy.
2. Gain Leadership Commitment and Build a Cross-Functional Team: Ensure leadership buy-in to help guide the process, manage funding, and gain visibility across teams. Next, a task force consisting of representatives from all key departments will be put together.
3. Develop a Unified GRC Framework: Select the right GRC framework for the organization based on its needs and industry. Standardize and document the various roles and processes needed to align governance, risk, and compliance activities.
4. Implement Technology Solutions: Invest in the right GRC tools that will help with both integration and automation. Next, consolidate all relevant data for complete visibility and analysis. Finally, integrate existing organizational systems with the chosen GRC solution.
5. Train Employees and Foster a Risk-Aware Culture: Ensure employees are trained on GRC principles and their role in its implementation and management. Encourage employees to take accountability and proactively identify and report issues.
6. Monitor, Audit, and Optimize: Define measurable metrics to track the success of implementation. Periodically review these metrics to ensure their effectiveness, and use feedback and audit reports to refine and modify GRC processes in an ongoing manner.
7. Communicate Progress to Stakeholders: Share both positive and negative outcomes with the relevant stakeholders to ensure transparency. Their input can also help with aligning the process to the organization’s needs and external requirements.
We, at MetricStream, understand the importance of an integrated and connected approach to bring together all three GRC elements - governance, risk, and compliance - to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving risk landscape.
MetricStream Business GRC enables organizations to adopt a holistic and connected approach to managing risks, regulatory requirements, audits, and third parties. Standardized GRC taxonomies and a consistent approach enable seamless collaboration across teams, simplifying the process of collecting and analyzing risk, compliance, audit, and third-party vendor data from across the enterprise for actionable insights. This provides an organization with a single source of truth and enables them to understand the interconnectedness of risks. Enriched with AI capabilities and advanced risk analytics, BusinessGRC is designed to help organizations keep up with the fast-changing risk and regulatory environment and improve their preparedness for unknown unknowns.
With MetricStream BusinessGRC, organizations can:
- Gain contextual risk and compliance information and predictive insights that can help strengthen the overall GRC posture.
- Accelerate decision-making through automated workflows and processes while reducing data redundancies and duplication of effort
- Create and maintain a gold source of data that drives effective firm-wide collaboration and coordination to identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
- Establish a robust and comprehensive foundation for good governance across the extended enterprise.
FAQ
What is the full form of GRC?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), and encompasses the tools and processes for identifying and managing risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and establishing good governance.
What is the difference between GRC and compliance?
GRC is an integrated approach to managing governance, risk, and compliance activities, while compliance is adhering to relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards.
What is the difference between GRC and ERM?
GRC refers to managing governance, risk, and compliance activities in a connected and coordinated manner, while ERM (enterprise risk management) is the process of identifying, assessing, managing and mitigating enterprise risks.








