Introduction
Picture this: An established company has discovered that its newly launched product is embroiled in a legal battle due to non-compliance with industry standards.
This scenario isn't uncommon; businesses across the globe face substantial fines and reputational damage due to lapses in compliance. Organizations must ensure adherence to a myriad of regulations and standards. Effective compliance controls are the mechanisms that organizations implement to achieve this crucial objective.
Key Takeaways
- Compliance controls are essential for ensuring that businesses adhere to laws, regulations, and internal policies, thus preventing legal issues and safeguarding the organization’s reputation.
- There are three main types of compliance controls: preventive controls (to avert issues before they occur), detective controls (to identify issues post-occurrence), and corrective controls (to address and fix detected issues).
- Without effective compliance controls, businesses face regulatory penalties, reputational damage, operational inefficiencies, data breaches, employee misconduct, financial losses, and strategic misalignment.
- Integrating compliance controls enhances risk mitigation, data-driven decision-making, transparency, accountability, internal controls, and stakeholder confidence.
- To effectively implement compliance controls, conduct risk assessments, engage stakeholders, document policies, assign responsibilities, provide training, and monitor controls regularly through audits and assessments.
What are Compliance Controls?
Compliance controls are mechanisms, policies, and procedures an organization implements to ensure adherence to laws, regulations, and internal standards. These controls aim to detect, prevent, and rectify non-compliance issues that can arise in various aspects of business operations, from financial reporting to data security. They form the backbone of a company's risk management strategy, providing a structured approach to minimize risks and safeguard the organization's integrity.
Types of Compliance Controls
The three main types of compliance controls are preventive, detective, and corrective. Preventive controls, like training programs, aim to prevent issues. Detective controls, such as audits, identify issues after they occur. Corrective controls address and fix detected issues, ensuring long-term compliance.
Here’s a deeper dive into the three main types of compliance controls:
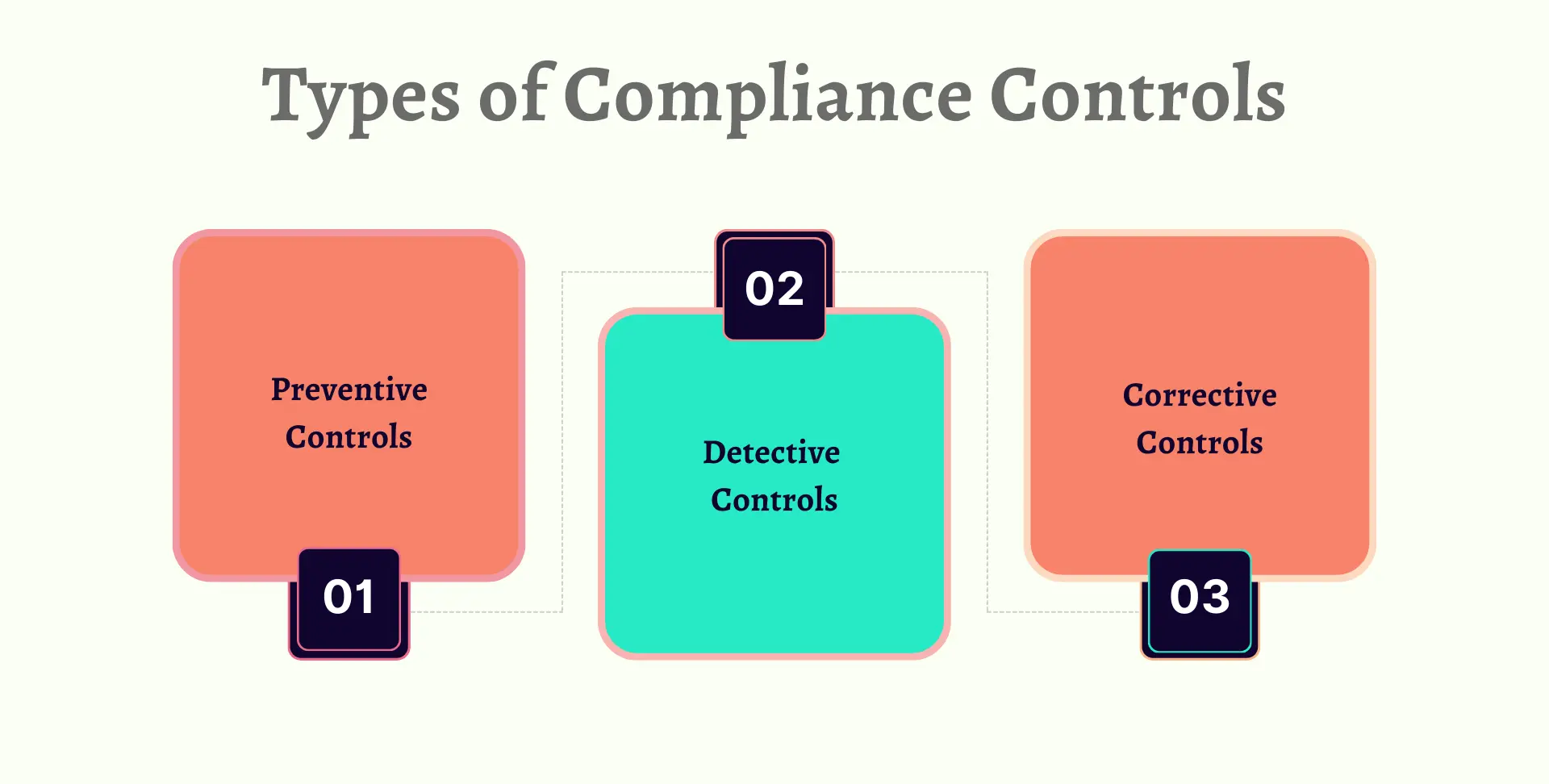
Preventive Controls
Preventive controls are designed to avert compliance issues before they occur. They can be established in accordance with the company's risk profile and aim to ensure that business processes and operations are conducted according to regulatory requirements and internal policies. Examples include employee training programs, access control mechanisms, and automated systems that flag potential compliance breaches.
By establishing a robust framework of preventive controls, organizations can proactively manage risks, reduce the likelihood of non-compliance, and foster a culture of ethical behavior and accountability. These controls are essential for setting the right tone at the top and ensuring that compliance is integrated into the business's daily operations.
Detective Controls
Detective controls are mechanisms put in place to identify and flag non-compliance incidents after they have occurred. They act as a second line of defense by monitoring and detecting irregularities, errors, or breaches. Common examples include audits, compliance reviews, continuous monitoring systems, and exception reports.
Detective controls are crucial for understanding compliance lapses and providing insights into areas that require improvement. They enable organizations to react promptly to compliance issues, thereby minimizing potential damage. Effective detective controls also serve as a feedback loop for refining preventive measures and enhancing the overall compliance framework.
Corrective Controls
Corrective controls are implemented to address and rectify non-compliance incidents once they have been detected. These controls focus on remedying the immediate issue and preventing future occurrences. Examples include disciplinary actions, process redesign, additional training, and implementing stronger preventive measures.
Corrective controls are vital for maintaining the integrity of the compliance program and demonstrating a commitment to regulatory adherence. They help organizations learn from their mistakes, reinforce compliance standards, and continuously improve their compliance processes. By promptly addressing compliance failures, organizations can mitigate the impact of such incidents and strengthen their resilience against future risks.
Risks of Not Incorporating Controls in Risk and Compliance Processes
Below are some potential risks companies can face if they fail to embed compliance controls into their daily business operations:
- Regulatory Penalties and Fines: Without embedded controls, organizations are at a higher risk of non-compliance, which can lead to hefty fines and penalties from regulatory bodies. These financial repercussions can severely impact an organization's bottom line.
- Reputational Damage: Failure to maintain compliance can significantly damage an organization's reputation. Loss of customer trust and negative media coverage can have long-lasting effects on the brand.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Lack of structured controls can lead to chaotic and inefficient processes, resulting in wasted resources, time delays, and increased operational costs.
- Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats: Without proper controls, sensitive data may be exposed to breaches and cyber-attacks, leading to severe legal and financial consequences and loss of stakeholder trust.
- Employee Misconduct: The absence of embedded compliance controls may create an environment where unethical behavior goes unchecked, increasing the likelihood of fraud, embezzlement, and other misconduct.
- Financial Losses: Ineffective compliance controls can lead to direct financial losses through fines and lawsuits, as well as indirect losses due to inefficiencies and reputational damage.
- Misaligned Business Strategies: A lack of embedded controls can result in misalignment between business strategies and compliance requirements, causing strategic initiatives to falter or fail.
Importance of Embedding Compliance Controls into Risk and Compliance Processes
Embedding controls into your organization's risk and compliance processes can offer a range of advantages. Here's a detailed look at the benefits you can expect:
- Enhanced Risk Mitigation: Integrating compliance controls allows for proactive identification and management of risks. By including these controls within the risk framework, organizations can detect potential risks earlier and take corrective action before they escalate.
- Compliance By Design: Embedding compliance controls into processes helps implement ‘compliance by design’. This enables organizations to ensure that their processes are aligned to relevant regulatory requirements from the very beginning.
- Reduced Risk of Non-Compliance: By embedding compliance controls, organizations adopt a compliance-first strategy and not treat it as an afterthought. This helps lower their compliance costs, reduce their noncompliance risk and free-up their personnel to focus on activities that deliver real benefit to the bottom line.
- Enhanced Visibility: The integrated approach helps improve visibility into the organization’s overall risk and compliance posture. When supported with technology-driven tools and software solutions, it helps organizations to automate the testing of these controls to proactively identify and address control gaps and weakness.
- Better Transparency and Accountability: Including compliance controls in the risk and compliance frameworks helps achieve high level of efficiency, agility, accountability, and transparency. It helps ensure clear understanding by every relevant role, delivers it within the organization in a consistent and unified way, tracks non-compliance, and puts in place an immediate corrective action plan.
- Better Stakeholder Confidence: Embedding compliance controls ensures that internal control systems are robust, streamlined, and aligned with business objectives. This leads to improved governance and internal audit functions and better trust and confidence with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators.
How to Implement Compliance Controls Effectively?
Here are some practical tips to implement compliance controls:
- Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Begin by thoroughly assessing your organization's risks. Identify areas where compliance controls are necessary and understand the potential impact of these risks.
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve key stakeholders, including senior management, compliance officers, and department heads, in the planning and implementation process. Their buy-in is crucial for successful integration and adherence.
- Develop and Document Policies and Procedures: Create detailed policies and procedures that outline the compliance controls. Ensure these documents are accessible to all employees and provide clear guidance on how to follow the controls.
- Assign Responsibilities: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for implementing and monitoring compliance controls. Ensure that everyone understands their part in maintaining compliance and managing risks.
- Provide Training and Education: Offer comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees understand the importance of compliance controls and know how to implement them correctly.
- Monitor and Test Controls Regularly: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your controls through regular audits and assessments. Make adjustments as needed to address any weaknesses or gaps.
- Conduct Periodic audits and Reviews: Schedule regular internal audits and reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of your compliance controls. Use audit findings to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Conclusion
Effective compliance controls are the backbone of a resilient and trustworthy organization. By understanding the importance of each component of the compliance framework and leveraging advanced GRC solutions like MetricStream, organizations can achieve a robust compliance posture that safeguards against risks and promotes sustainable growth.
Picture this: An established company has discovered that its newly launched product is embroiled in a legal battle due to non-compliance with industry standards.
This scenario isn't uncommon; businesses across the globe face substantial fines and reputational damage due to lapses in compliance. Organizations must ensure adherence to a myriad of regulations and standards. Effective compliance controls are the mechanisms that organizations implement to achieve this crucial objective.
- Compliance controls are essential for ensuring that businesses adhere to laws, regulations, and internal policies, thus preventing legal issues and safeguarding the organization’s reputation.
- There are three main types of compliance controls: preventive controls (to avert issues before they occur), detective controls (to identify issues post-occurrence), and corrective controls (to address and fix detected issues).
- Without effective compliance controls, businesses face regulatory penalties, reputational damage, operational inefficiencies, data breaches, employee misconduct, financial losses, and strategic misalignment.
- Integrating compliance controls enhances risk mitigation, data-driven decision-making, transparency, accountability, internal controls, and stakeholder confidence.
- To effectively implement compliance controls, conduct risk assessments, engage stakeholders, document policies, assign responsibilities, provide training, and monitor controls regularly through audits and assessments.
Compliance controls are mechanisms, policies, and procedures an organization implements to ensure adherence to laws, regulations, and internal standards. These controls aim to detect, prevent, and rectify non-compliance issues that can arise in various aspects of business operations, from financial reporting to data security. They form the backbone of a company's risk management strategy, providing a structured approach to minimize risks and safeguard the organization's integrity.
The three main types of compliance controls are preventive, detective, and corrective. Preventive controls, like training programs, aim to prevent issues. Detective controls, such as audits, identify issues after they occur. Corrective controls address and fix detected issues, ensuring long-term compliance.
Here’s a deeper dive into the three main types of compliance controls:

Preventive Controls
Preventive controls are designed to avert compliance issues before they occur. They can be established in accordance with the company's risk profile and aim to ensure that business processes and operations are conducted according to regulatory requirements and internal policies. Examples include employee training programs, access control mechanisms, and automated systems that flag potential compliance breaches.
By establishing a robust framework of preventive controls, organizations can proactively manage risks, reduce the likelihood of non-compliance, and foster a culture of ethical behavior and accountability. These controls are essential for setting the right tone at the top and ensuring that compliance is integrated into the business's daily operations.
Detective Controls
Detective controls are mechanisms put in place to identify and flag non-compliance incidents after they have occurred. They act as a second line of defense by monitoring and detecting irregularities, errors, or breaches. Common examples include audits, compliance reviews, continuous monitoring systems, and exception reports.
Detective controls are crucial for understanding compliance lapses and providing insights into areas that require improvement. They enable organizations to react promptly to compliance issues, thereby minimizing potential damage. Effective detective controls also serve as a feedback loop for refining preventive measures and enhancing the overall compliance framework.
Corrective Controls
Corrective controls are implemented to address and rectify non-compliance incidents once they have been detected. These controls focus on remedying the immediate issue and preventing future occurrences. Examples include disciplinary actions, process redesign, additional training, and implementing stronger preventive measures.
Corrective controls are vital for maintaining the integrity of the compliance program and demonstrating a commitment to regulatory adherence. They help organizations learn from their mistakes, reinforce compliance standards, and continuously improve their compliance processes. By promptly addressing compliance failures, organizations can mitigate the impact of such incidents and strengthen their resilience against future risks.
Below are some potential risks companies can face if they fail to embed compliance controls into their daily business operations:
- Regulatory Penalties and Fines: Without embedded controls, organizations are at a higher risk of non-compliance, which can lead to hefty fines and penalties from regulatory bodies. These financial repercussions can severely impact an organization's bottom line.
- Reputational Damage: Failure to maintain compliance can significantly damage an organization's reputation. Loss of customer trust and negative media coverage can have long-lasting effects on the brand.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Lack of structured controls can lead to chaotic and inefficient processes, resulting in wasted resources, time delays, and increased operational costs.
- Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats: Without proper controls, sensitive data may be exposed to breaches and cyber-attacks, leading to severe legal and financial consequences and loss of stakeholder trust.
- Employee Misconduct: The absence of embedded compliance controls may create an environment where unethical behavior goes unchecked, increasing the likelihood of fraud, embezzlement, and other misconduct.
- Financial Losses: Ineffective compliance controls can lead to direct financial losses through fines and lawsuits, as well as indirect losses due to inefficiencies and reputational damage.
- Misaligned Business Strategies: A lack of embedded controls can result in misalignment between business strategies and compliance requirements, causing strategic initiatives to falter or fail.
Embedding controls into your organization's risk and compliance processes can offer a range of advantages. Here's a detailed look at the benefits you can expect:
- Enhanced Risk Mitigation: Integrating compliance controls allows for proactive identification and management of risks. By including these controls within the risk framework, organizations can detect potential risks earlier and take corrective action before they escalate.
- Compliance By Design: Embedding compliance controls into processes helps implement ‘compliance by design’. This enables organizations to ensure that their processes are aligned to relevant regulatory requirements from the very beginning.
- Reduced Risk of Non-Compliance: By embedding compliance controls, organizations adopt a compliance-first strategy and not treat it as an afterthought. This helps lower their compliance costs, reduce their noncompliance risk and free-up their personnel to focus on activities that deliver real benefit to the bottom line.
- Enhanced Visibility: The integrated approach helps improve visibility into the organization’s overall risk and compliance posture. When supported with technology-driven tools and software solutions, it helps organizations to automate the testing of these controls to proactively identify and address control gaps and weakness.
- Better Transparency and Accountability: Including compliance controls in the risk and compliance frameworks helps achieve high level of efficiency, agility, accountability, and transparency. It helps ensure clear understanding by every relevant role, delivers it within the organization in a consistent and unified way, tracks non-compliance, and puts in place an immediate corrective action plan.
- Better Stakeholder Confidence: Embedding compliance controls ensures that internal control systems are robust, streamlined, and aligned with business objectives. This leads to improved governance and internal audit functions and better trust and confidence with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and regulators.
Here are some practical tips to implement compliance controls:
- Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Begin by thoroughly assessing your organization's risks. Identify areas where compliance controls are necessary and understand the potential impact of these risks.
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve key stakeholders, including senior management, compliance officers, and department heads, in the planning and implementation process. Their buy-in is crucial for successful integration and adherence.
- Develop and Document Policies and Procedures: Create detailed policies and procedures that outline the compliance controls. Ensure these documents are accessible to all employees and provide clear guidance on how to follow the controls.
- Assign Responsibilities: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for implementing and monitoring compliance controls. Ensure that everyone understands their part in maintaining compliance and managing risks.
- Provide Training and Education: Offer comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees understand the importance of compliance controls and know how to implement them correctly.
- Monitor and Test Controls Regularly: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your controls through regular audits and assessments. Make adjustments as needed to address any weaknesses or gaps.
- Conduct Periodic audits and Reviews: Schedule regular internal audits and reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of your compliance controls. Use audit findings to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Effective compliance controls are the backbone of a resilient and trustworthy organization. By understanding the importance of each component of the compliance framework and leveraging advanced GRC solutions like MetricStream, organizations can achieve a robust compliance posture that safeguards against risks and promotes sustainable growth.








