Introduction
In today’s regulatory environment, businesses must navigate a complex web of laws and regulations to maintain compliance and avoid penalties. As per a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of non-compliance costs an average of $14 million dollars to organizations.
Compliance frameworks provide a structured approach to help organizations manage and adhere to these regulatory requirements, reducing not just the cost of non-compliance but also other associated compliance risks. These frameworks are essential tools that ensure businesses operate within the bounds of the law while maintaining ethical standards. Here, we delve into the key elements of compliance frameworks, provide details about prominent frameworks, and highlight the benefits and implementation of frameworks.
Key Takeaways
Definition:
A compliance framework helps organizations manage regulatory requirements systematically.
Elements:
Key elements include policies, procedures, training, monitoring, and reporting.
Examples:
AML, FCPA, CCPA, Anti-Corruption, HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, NIST CSF, KYC.
Consequences:
Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Implementation:
Involves risk assessment, policy development, training, and continuous monitoring.
Benefits:
Ensures legal compliance, reduces risk and promotes ethical business practices.
What is a Compliance Framework?
A compliance framework is a structured approach involving a set of policies, procedures, and controls that ensure organizations meet the mandated regulations and standards. A compliance framework is essential for organizations to comprehend their responsibilities, establish effective controls, and showcase compliance to stakeholders.
A compliance framework ensures that an organization follows not only external regulations (such as industry-specific laws, international standards, and government mandates) but also internal policies (like codes of conduct and corporate governance guidelines).
Compliance Framework Elements
A strong compliance framework typically includes several key elements:
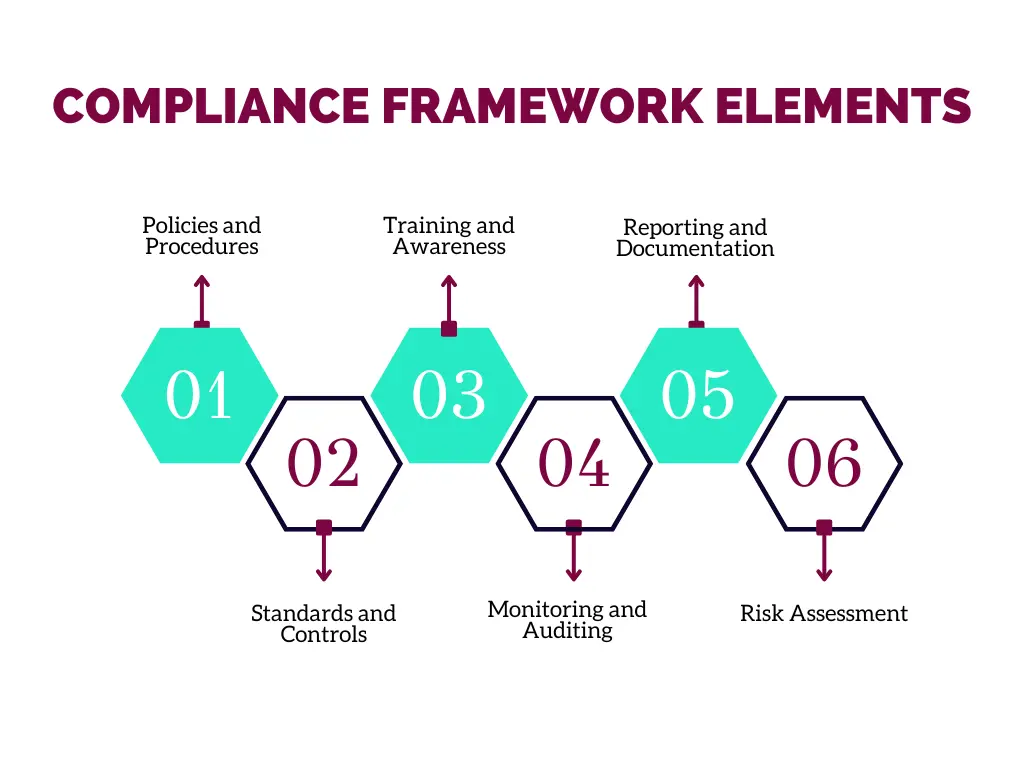
Policies and Procedures:
These documents outline the organization’s commitment to compliance and provide detailed instructions on how to adhere to regulations.
Standards and Controls:
Benchmarks and mechanisms for measuring compliance and implementing necessary controls to mitigate risks.
Training and Awareness:
Regular training sessions help employees understand compliance requirements and their roles in maintaining compliance.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Continuous monitoring and periodic audits ensure that compliance measures are effective and identify areas for improvement.
Reporting and Documentation:
Keeping detailed records of compliance activities and incidents helps demonstrate adherence to regulations and facilitates audits.
Risk Assessment:
Regular assessments help identify potential compliance risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Each of these elements plays a crucial role in creating a comprehensive and effective compliance framework, ensuring that the organization can consistently meet regulatory requirements.
List of Comprehensive Compliance Frameworks Organizations
Currently, there are various compliance frameworks that cater to different industries and regulatory needs. Here are some prominent frameworks:
General Frameworks
1. AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) frameworks are designed to detect and prevent financial crimes such as money laundering and terrorist financing. They require financial institutions to implement rigorous customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting mechanisms.
Key Actions:
Customer Due Diligence (CDD):
Financial institutions must verify the identity of their customers through documentation and ongoing monitoring.
Transaction Monitoring:
Implement systems to monitor and flag suspicious transactions in real time.
Reporting:
Institutions must report suspicious activities to relevant authorities, such as filing Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
2. FCPA (Foreign Corrupt Practices Act)
The FCPA framework helps organizations prevent and address corruption and bribery in international business transactions.
Key Actions:
Accurate Books and Records:
Maintain precise financial records to reflect transactions accurately.
Internal Controls:
Implement internal accounting controls to ensure compliance with anti-bribery laws.
Due Diligence:
Conduct thorough due diligence on third parties and business partners.
Industry-Specific Frameworks
1. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
The CCPA enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California.
Key Actions:
Data Disclosure:
Businesses must disclose their data collection practices to consumers.
Opt-Out Options:
Provide consumers with the ability to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
Data Security:
Implement measures to protect consumer data from unauthorized access and breaches.
2. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA compliance frameworks protect sensitive patient information in healthcare organizations.
Key Actions:
Privacy Rule:
Ensure that patient information is disclosed only for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
Security Rule:
Implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to secure electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Breach Notification Rule:
Notify affected individuals and authorities in the event of a data breach involving ePHI.
3. PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The PCI DSS framework ensures that organizations handling credit card information maintain a secure environment.
Key Actions:
Secure Network:
Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data.
Data Protection:
Safeguard stored cardholder data and encrypt the transmission of cardholder data over open networks.
Access Control:
Restrict access to cardholder data to only those whose job requires it.
4. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation for organizations handling the personal data of EU residents.
Key Actions:
Consent:
Obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their personal data.
Data Protection:
Implement technical and organizational measures to ensure data security.
Data Subject Rights:
Facilitate data access, rectification, and deletion requests from individuals.
5. NIST CSF (National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework)
The NIST CSF provides a policy framework to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks
Key Actions:
Identify:
Develop an understanding of the organizational context and risks.
Protect:
Implement safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services.
Detect:
Develop activities to identify the occurrence of cybersecurity events.
Respond:
Create plans to respond to detected cybersecurity incidents.
Recover:
Implement strategies to restore capabilities or services impaired by cybersecurity incidents.
6. KYC (Know Your Customer)
KYC frameworks are crucial for financial institutions to verify client identities and assess the risk of illegal activities.
Key Actions:
Customer Identification Program (CIP):
Collect and verify customer identification information.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD):
Conduct background checks and risk assessments on customers.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD):
Apply additional scrutiny to high-risk customers and transactions.
What are the Consequences of Non-compliance?
Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can lead to severe consequences, including:
Financial Penalties:
Organizations may face substantial fines and penalties for failing to comply with regulations. For example, GDPR violations can result in fines of up to 2% of annual global turnover or €10 million, whichever is higher.
Legal Action:
Non-compliance can lead to legal proceedings, which can be costly and time-consuming. In cases of severe violations, companies may also face criminal charges.
Reputational Damage:
Publicized non-compliance incidents can harm an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
Operational Disruptions:
Non-compliance can result in operational disruptions, such as the suspension of business activities, which can impact productivity and profitability.
How to Implement a Compliance Framework
Implementing a compliance framework involves several key steps:
Risk Assessment:
Conduct a thorough assessment to identify potential compliance risks and vulnerabilities.
Policy Development:
Develop and document policies and procedures that outline compliance requirements and guidelines.
Training and Awareness:
Educate employees on compliance policies and their roles in maintaining compliance through regular training sessions.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring and periodic auditing to ensure compliance measures are effective.
Reporting and Documentation:
Maintain detailed records of compliance activities and incidents to facilitate audits and demonstrate adherence to regulations.
Continuous Improvement:
Regularly review and update compliance policies and procedures to address emerging risks and regulatory changes.
The Advantages of Implementing Compliance Frameworks
As per a report by Thomson Reuters, more than 65% of organizations believe that streamlining and automating processes would help them reduce complexity and cost of risk and compliance.
Implementing compliance frameworks offers numerous benefits, including:
Legal Compliance:
Ensures that the organization adheres to all relevant laws and regulations, avoiding penalties and legal actions.
Risk Management:
Identifies and mitigates compliance risks, reducing the likelihood of incidents and their impact.
Operational Efficiency:
Streamlines processes and procedures, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Reputation Protection:
Maintains and enhances the organization’s reputation by demonstrating a commitment to ethical and compliant business practices.
Customer Trust:
Builds and maintains customer trust by protecting their data and ensuring transparent business practices.
How MetricStream Compliance Management Can Help
MetricStream Compliance Management offers comprehensive solutions to help organizations implement and maintain effective compliance frameworks. Our platform provides tools for risk assessment, policy management, training, monitoring, and reporting.
With MetricStream’s solutions, businesses can streamline their compliance processes, ensure adherence to regulations, and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Conclusion
Compliance frameworks are essential for organizations to navigate the complex regulatory landscape and maintain ethical business practices. By understanding the key elements of compliance frameworks and implementing them effectively, businesses can ensure legal compliance, manage risks, and protect their reputation.
Reach out to us, to streamline your compliance efforts and focus on growth and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a compliance framework?
A compliance framework is a structured set of guidelines that help organizations manage regulatory requirements systematically. It provides a methodical approach to identifying, monitoring, and mitigating compliance risks, ensuring that businesses operate within legal boundaries and maintain ethical standards. 2.
Why is implementing a compliance framework important?
Implementing a compliance framework is crucial because it helps organizations avoid legal penalties, manage risks, enhance operational efficiency, and protect their reputation.
What are the key elements of a strong compliance framework?
The key elements of a strong compliance framework include policies and procedures, training and awareness, monitoring and auditing, reporting and documentation, and risk assessment..
In today’s regulatory environment, businesses must navigate a complex web of laws and regulations to maintain compliance and avoid penalties. As per a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of non-compliance costs an average of $14 million dollars to organizations.
Compliance frameworks provide a structured approach to help organizations manage and adhere to these regulatory requirements, reducing not just the cost of non-compliance but also other associated compliance risks. These frameworks are essential tools that ensure businesses operate within the bounds of the law while maintaining ethical standards. Here, we delve into the key elements of compliance frameworks, provide details about prominent frameworks, and highlight the benefits and implementation of frameworks.
Definition:
A compliance framework helps organizations manage regulatory requirements systematically.
Elements:
Key elements include policies, procedures, training, monitoring, and reporting.
Examples:
AML, FCPA, CCPA, Anti-Corruption, HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, NIST CSF, KYC.
Consequences:
Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Implementation:
Involves risk assessment, policy development, training, and continuous monitoring.
Benefits:
Ensures legal compliance, reduces risk and promotes ethical business practices.
A compliance framework is a structured approach involving a set of policies, procedures, and controls that ensure organizations meet the mandated regulations and standards. A compliance framework is essential for organizations to comprehend their responsibilities, establish effective controls, and showcase compliance to stakeholders.
A compliance framework ensures that an organization follows not only external regulations (such as industry-specific laws, international standards, and government mandates) but also internal policies (like codes of conduct and corporate governance guidelines).
A strong compliance framework typically includes several key elements:

Policies and Procedures:
These documents outline the organization’s commitment to compliance and provide detailed instructions on how to adhere to regulations.
Standards and Controls:
Benchmarks and mechanisms for measuring compliance and implementing necessary controls to mitigate risks.
Training and Awareness:
Regular training sessions help employees understand compliance requirements and their roles in maintaining compliance.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Continuous monitoring and periodic audits ensure that compliance measures are effective and identify areas for improvement.
Reporting and Documentation:
Keeping detailed records of compliance activities and incidents helps demonstrate adherence to regulations and facilitates audits.
Risk Assessment:
Regular assessments help identify potential compliance risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Each of these elements plays a crucial role in creating a comprehensive and effective compliance framework, ensuring that the organization can consistently meet regulatory requirements.
Currently, there are various compliance frameworks that cater to different industries and regulatory needs. Here are some prominent frameworks:
General Frameworks
1. AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) frameworks are designed to detect and prevent financial crimes such as money laundering and terrorist financing. They require financial institutions to implement rigorous customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting mechanisms.
Key Actions:
Customer Due Diligence (CDD):
Financial institutions must verify the identity of their customers through documentation and ongoing monitoring.
Transaction Monitoring:
Implement systems to monitor and flag suspicious transactions in real time.
Reporting:
Institutions must report suspicious activities to relevant authorities, such as filing Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
2. FCPA (Foreign Corrupt Practices Act)
The FCPA framework helps organizations prevent and address corruption and bribery in international business transactions.
Key Actions:
Accurate Books and Records:
Maintain precise financial records to reflect transactions accurately.
Internal Controls:
Implement internal accounting controls to ensure compliance with anti-bribery laws.
Due Diligence:
Conduct thorough due diligence on third parties and business partners.
Industry-Specific Frameworks
1. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
The CCPA enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California.
Key Actions:
Data Disclosure:
Businesses must disclose their data collection practices to consumers.
Opt-Out Options:
Provide consumers with the ability to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
Data Security:
Implement measures to protect consumer data from unauthorized access and breaches.
2. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA compliance frameworks protect sensitive patient information in healthcare organizations.
Key Actions:
Privacy Rule:
Ensure that patient information is disclosed only for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
Security Rule:
Implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to secure electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Breach Notification Rule:
Notify affected individuals and authorities in the event of a data breach involving ePHI.
3. PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The PCI DSS framework ensures that organizations handling credit card information maintain a secure environment.
Key Actions:
Secure Network:
Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data.
Data Protection:
Safeguard stored cardholder data and encrypt the transmission of cardholder data over open networks.
Access Control:
Restrict access to cardholder data to only those whose job requires it.
4. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation for organizations handling the personal data of EU residents.
Key Actions:
Consent:
Obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their personal data.
Data Protection:
Implement technical and organizational measures to ensure data security.
Data Subject Rights:
Facilitate data access, rectification, and deletion requests from individuals.
5. NIST CSF (National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework)
The NIST CSF provides a policy framework to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks
Key Actions:
Identify:
Develop an understanding of the organizational context and risks.
Protect:
Implement safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services.
Detect:
Develop activities to identify the occurrence of cybersecurity events.
Respond:
Create plans to respond to detected cybersecurity incidents.
Recover:
Implement strategies to restore capabilities or services impaired by cybersecurity incidents.
6. KYC (Know Your Customer)
KYC frameworks are crucial for financial institutions to verify client identities and assess the risk of illegal activities.
Key Actions:
Customer Identification Program (CIP):
Collect and verify customer identification information.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD):
Conduct background checks and risk assessments on customers.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD):
Apply additional scrutiny to high-risk customers and transactions.
Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can lead to severe consequences, including:
Financial Penalties:
Organizations may face substantial fines and penalties for failing to comply with regulations. For example, GDPR violations can result in fines of up to 2% of annual global turnover or €10 million, whichever is higher.
Legal Action:
Non-compliance can lead to legal proceedings, which can be costly and time-consuming. In cases of severe violations, companies may also face criminal charges.
Reputational Damage:
Publicized non-compliance incidents can harm an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
Operational Disruptions:
Non-compliance can result in operational disruptions, such as the suspension of business activities, which can impact productivity and profitability.
Implementing a compliance framework involves several key steps:
Risk Assessment:
Conduct a thorough assessment to identify potential compliance risks and vulnerabilities.
Policy Development:
Develop and document policies and procedures that outline compliance requirements and guidelines.
Training and Awareness:
Educate employees on compliance policies and their roles in maintaining compliance through regular training sessions.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring and periodic auditing to ensure compliance measures are effective.
Reporting and Documentation:
Maintain detailed records of compliance activities and incidents to facilitate audits and demonstrate adherence to regulations.
Continuous Improvement:
Regularly review and update compliance policies and procedures to address emerging risks and regulatory changes.
As per a report by Thomson Reuters, more than 65% of organizations believe that streamlining and automating processes would help them reduce complexity and cost of risk and compliance.
Implementing compliance frameworks offers numerous benefits, including:
Legal Compliance:
Ensures that the organization adheres to all relevant laws and regulations, avoiding penalties and legal actions.
Risk Management:
Identifies and mitigates compliance risks, reducing the likelihood of incidents and their impact.
Operational Efficiency:
Streamlines processes and procedures, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Reputation Protection:
Maintains and enhances the organization’s reputation by demonstrating a commitment to ethical and compliant business practices.
Customer Trust:
Builds and maintains customer trust by protecting their data and ensuring transparent business practices.
MetricStream Compliance Management offers comprehensive solutions to help organizations implement and maintain effective compliance frameworks. Our platform provides tools for risk assessment, policy management, training, monitoring, and reporting.
With MetricStream’s solutions, businesses can streamline their compliance processes, ensure adherence to regulations, and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Compliance frameworks are essential for organizations to navigate the complex regulatory landscape and maintain ethical business practices. By understanding the key elements of compliance frameworks and implementing them effectively, businesses can ensure legal compliance, manage risks, and protect their reputation.
Reach out to us, to streamline your compliance efforts and focus on growth and innovation.
What is a compliance framework?
A compliance framework is a structured set of guidelines that help organizations manage regulatory requirements systematically. It provides a methodical approach to identifying, monitoring, and mitigating compliance risks, ensuring that businesses operate within legal boundaries and maintain ethical standards. 2.
Why is implementing a compliance framework important?
Implementing a compliance framework is crucial because it helps organizations avoid legal penalties, manage risks, enhance operational efficiency, and protect their reputation.
What are the key elements of a strong compliance framework?
The key elements of a strong compliance framework include policies and procedures, training and awareness, monitoring and auditing, reporting and documentation, and risk assessment..








