Introduction
2023 was marked by continuing disruption, economic concerns, and tension and turbulence around the world, adding to an already fraught risk landscape. Intensifying geopolitical conflicts, economic slowdown, a rapidly evolving technology landscape, increasing regulatory pressure, and lack of skilled talent are adding to the cyber risk management challenge. Cyberattacks increased by 38 percent this year compared to the last, and the cyber risk landscape will continue to evolve and grow in complexity in 2024.
2023 was the year of generative AI. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) took the power of AI mainstream, creating innumerable opportunities for industries to scale up and accelerate their digital innovation journeys. However, AI technologies in the wrong hands pose significant cyber risks for enterprises. 46 percent of CISOs now say that AI technologies rank amongst the top cyber risks facing their organizations. Attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated as bad actors have easy access to AI technologies for perpetuating deep fakes, attacking IoT devices, and even carrying out system impersonation. This necessitates a more robust and AI-powered cyber risk management approach. Keeping up with the pace of regulatory change is another area of concern as regulators worldwide try to keep pace with the disruption and instability in the larger environment.
Most business and cyber leaders believe that the threat landscape and the nature of cyber threats are not only increasing, but also changing rapidly. The focus is shifting to disrupting business and damaging reputation. 58 percent of CISOs believe that cyber risks will continue to change quickly and that enterprises will be facing a new set of risks in the next five years.
A robust cyber governance, risk, and compliance (Cyber GRC) program is now more important than ever. At the same time, the overarching enterprise risk management strategy must be agile and scalable enough to address emerging risks and new threats to the enterprise as they occur. Understanding 2023’s cyber risk trends is important for businesses to prepare for and successfully navigate the ever-evolving risk landscape in 2024.
MetricStream remains committed to helping enterprises effectively navigate cyber risk amidst disruption and instability. Based on our interactions with customers, security leaders, industry leaders, and market research, we have collated the top 7 cyber risk trends that can help shape your risk management strategy in 2024.
What’s Next in 2024?
1. Next-Generation AI-Powered Risk Management Tools
Artificial intelligence holds significant potential for building robust cyber risk management strategies that can address new sophisticated threats.
Enterprises are leveraging AI to build intelligent, secure, and automated systems that can detect, prevent, and even predict new attacks in real time, to help enterprises address threats immediately. From natural language processing, assisted and automated workflows, machine learning, and face detection to automatic threat detection, AI-powered cyber risk tools can equip organizations to stay on top of these emerging risks and threats in the AI era.
34 percent of organizations are already using AI security tools for risk management, while 56 percent are actively exploring AI solutions. Leveraging AI capabilities can help optimize cyber risk and IT compliance management processes with faster and more accurate insights into the control environment, automated control testing coupled with intelligent classification and remediation of issues, intent-based policy search, predictive and remedial analytics, scenario simulation, and much more. And all this is just the tip of the iceberg as the true potential of AI will unravel over the coming years. As the risk landscape continues to grow in complexity, AI-powered risk management tools will be indispensable for identifying and mitigating new-age threats.
2. Autonomous Risk Assessment for Improved Accuracy in Decision-Making
Cyber risk quantification and assessment methods help organizations evaluate monetary risk exposure, and effectively communicate the risks, so that the C-suite can make informed business decisions. However, the methodology so far has been largely centered around the scenario-based approach, which is not only unrelated to real-world scenarios but also heavily reliant on extensive data entry, making it complex, not automated, and difficult to scale. As the cyber risk landscape continues to evolve, enterprises need tools that can ensure continuous accurate risk assessments and quantification.
Asset value-based risk quantification enables organizations to take an automated and continuous approach to risk assessments based on the value of the assets and the type of risks they’re exposed to. All asset values and their weighted risk exposures are considered to arrive at a standardized, actionable risk score that can be used to easily prioritize risks.
This approach offers the flexibility to change risk factors for more accurate and optimized decision-making. The weightage assigned to a risk can be changed based on the changing business landscape and needs. The scoring methodology is autonomous and runs continuously to incorporate data changes as risks are evaluated, which ensures accurate results. With this approach, risk managers can quickly and accurately identify which parts of the organization are exposed to critical risks and make immediate informed decisions to address the risks. Further with the introduction of AI technologies into these quantification methods, the true benefits are yet to be seen.
3. Increasing Regulatory Obligations and the Promise of Automated Compliance
Alarmed at the increase of cyber threats and the impact they may have on the entire ecosystem, regulators around the world are increasingly focussing on introducing stringent regulations and laws pertaining to cyber risk management and security. This appears to be a new trend of issuing direct regulations focussed on cyber security and risk management, instead of the erstwhile practice of issuing guidelines and letting enterprises implement risk management programs as per their internal strategies.
Most of the regulations being implemented require enterprises to implement robust risk management programs and report cyber incidents, risk management practices, and management expertise in place. This includes recent regulations like SEC cybersecurity rules for public companies in the U.S., the Digital Personal Data Protection Act in India, and the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and Cyber Resilience Act in the EU.
Keeping up with changing regulatory requirements without an automated and robust compliance platform can be difficult for organizations, some of whom run the risk of unwittingly failing to comply with a new legislation or regulation. Going forward, we expect to see growing adoption of software solutions that offer automated capabilities for regulatory horizon scanning, regulatory change management, control creation from regulations, continuous control monitoring, and control testing and evidence collection.
We expect to see growing adoption of such tools across industries, enabling organizations to continuously improve cyber risk and compliance posture and significantly reduce audit costs.
4. Sophisticated Attacks
Technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace today. And while there is no doubt that technology is a powerful force for good, it is also undeniable that the same technology can be used by bad actors to launch increasingly sophisticated attacks on enterprises. The emergence of generative AI in 2023 has upped enterprise cyber risk considerably.
Generative AI tools are already being used for phishing, identifying and exploiting IoT vulnerabilities, deepfakes, keystroke monitoring, malware, and ransomware. Advanced persistent threats and ransomware will also continue to be major cybersecurity issues. Attackers are using AI to analyze attack strategies before launching them and to increase the scale and speed of attacks. And they are using AI to evade existing security strategies and evade algorithms that detect suspicious activity. Such spoofing attempts are only going to evolve further.
Automated, AI-powered cyber risk management solutions are a business imperative today as the use of AI for malicious purposes will only increase in the future.
5. Third-Party Cyber Risk
More and more organizations are required to work with third-party vendors and manage external supply chains. As risks grow increasingly interconnected, they must extend cyber risk management strategies to third-party partners and supply chains as well. According to the 2022 Ponemon Institute State of Cybersecurity and Third-Party Remote Access Security Report, 49% of surveyed organizations said that they experienced third-party cyber attacks in the past year compared to 44% in the previous 12 months.
Cyber adversaries will continue to focus on exploiting supply chain vulnerabilities in 2024 by using new and powerful technologies and methods. Inadequate risk management and security strategies, lack of encryption, open-source software, vendor applications and software with inadequate security measures, and an exponential increase in AI-based malware pose significant risks to enterprises. Cyber criminals are likely to exploit the gaps in the connection network between suppliers, and service providers. Organizations must focus on managing third-party risks to improve their overall security posture and this need is continuously increasing as all IT systems have third-party components.
The aim of a third-party cyber risk management strategy is to recognize and address the business, operational, and cyber risks linked to third parties, and subsequent parties, including fourth parties and beyond. Enterprises need to ensure stringent scrutiny of third-party suppliers and implement robust third-party cyber risk assessments to protect themselves.
6. Rise in Cybersecurity Investments and Cybersecurity Insurance Costs
Organizational spending on cyber security and risk management was expected to touch USD 188. 1 billion in 2023. This is expected to increase by 14.3 percent to reach USD 215 billion in 2024 as organizations continue to recognize the increasing risk and costs of cyber-attacks. The key areas of investment include:
Cloud security: The cloud is the foundation for any digital transformation journey and most organizations are moving their data and applications to the cloud –private, public, and hybrid. While cloud adoption is critical for innovation, scalability, and agility, it is also susceptible to cyber attacks and data breaches. There is an upswing in investment in cloud security solutions such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), and cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools. This is expected to continue in 2024.
AI and ML: Enterprise cyber security strategies in the age of AI must include AI and ML-based solutions to fortify cyber defense. These technologies improve real-time detection and response to threats and are a critical investment at a time when cyber criminals are increasingly leveraging technology to launch sophisticated attacks. Investments in AI-powered security solutions, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat intelligence, and incident response automation, are likely to grow in 2024.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security: IoT devices are increasingly becoming ubiquitous across industries. And securing them is now a business imperative. Investments in IoT security solutions, such as device authentication, encryption, and segmentation, are expected to rise.
DevSecOps: The integration of security into DevOps practices, known as DevSecOps, is gaining traction. Investments in DevSecOps tools and services, such as container security, infrastructure as code (IaC), and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR), are anticipated to increase.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Workloads on the cloud are growing at unprecedented rates, generative AI is making further inroads into enterprise digital strategy and the number of IoT devices is increasing exponentially. Identity and access management is a crucial element of enterprise risk management strategies in this hyper-connected landscape. Investments in IAM solutions, such as identity governance, administration, and privileged access management (PAM), are expected to continue growing.
Endpoint Security: Hybrid working is here to stay resulting in a highly distributed enterprise IT with multiple endpoints, which is a popular attack vector for cybercriminals. Investments in endpoint security solutions, such as endpoint detection and response will continue to increase over the next year.
Integrated risk management (IRM): Technology has created a world that is more connected than ever before. Enterprise cyber risks and vulnerabilities cannot be assessed or mitigated effectively in isolation. Most organizations now consider IRM to be foundational to their cyber risk management strategy as it combines the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks along with managing and monitoring them. 2024 will see continuing investments in IRM solutions.
Cyber security insurance: Organizations are now operating in a significantly heightened risk environment. As a result, cyber risk insurance premiums are on the rise. Annual cyber insurance premiums are currently around USD 5 billion and this is expected to increase by 20- 30 percent year on year.
7. Insider Threats and the Importance of Risk-Aware Culture
Human error, callousness, and malintent remain the biggest reasons for any data breach. 74 percent of all data breaches in 2023 were directly or indirectly caused by internal personnel. Some were phishing or social engineering attacks, while others were caused by human errors or misuse.
Organizations must invest in creating a risk-aware culture through more frequent training and practical evaluations. This is not just within their own walls, but at their third-party vendors as well. Continuous training and awareness sessions are critical. It is equally important to equip the first line of defense with the skills and tools they need to identify, evaluate, and address cyber risk.
How MetricStream Can Help
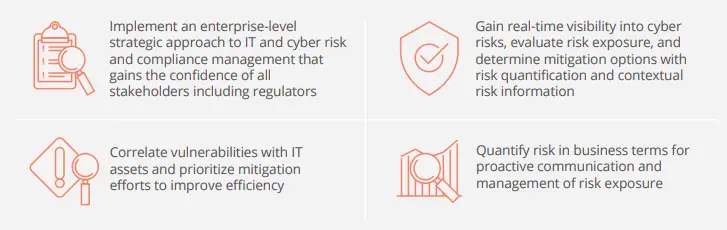
MetricStream CyberGRC enables organizations to proactively manage cyber risk and compliance with a comprehensive IT and Cyber Risk Compliance Framework that is aligned with established security standards.
With this framework, enterprises can manage IT and cyber risks more effectively, ensure compliance with all relevant regulations, manage third-party risks, and pass IT audits quickly. Organizations can also gain comprehensive insights into their overall IT risk and compliance landscape and secure the support of the leadership team by quantifying risk in business terms. They can leverage readily available industry benchmarks and rules such as ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and NIST SP800-53 to quickly connect rules to IT controls and policy exceptions.
2023 was marked by continuing disruption, economic concerns, and tension and turbulence around the world, adding to an already fraught risk landscape. Intensifying geopolitical conflicts, economic slowdown, a rapidly evolving technology landscape, increasing regulatory pressure, and lack of skilled talent are adding to the cyber risk management challenge. Cyberattacks increased by 38 percent this year compared to the last, and the cyber risk landscape will continue to evolve and grow in complexity in 2024.
2023 was the year of generative AI. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) took the power of AI mainstream, creating innumerable opportunities for industries to scale up and accelerate their digital innovation journeys. However, AI technologies in the wrong hands pose significant cyber risks for enterprises. 46 percent of CISOs now say that AI technologies rank amongst the top cyber risks facing their organizations. Attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated as bad actors have easy access to AI technologies for perpetuating deep fakes, attacking IoT devices, and even carrying out system impersonation. This necessitates a more robust and AI-powered cyber risk management approach. Keeping up with the pace of regulatory change is another area of concern as regulators worldwide try to keep pace with the disruption and instability in the larger environment.
Most business and cyber leaders believe that the threat landscape and the nature of cyber threats are not only increasing, but also changing rapidly. The focus is shifting to disrupting business and damaging reputation. 58 percent of CISOs believe that cyber risks will continue to change quickly and that enterprises will be facing a new set of risks in the next five years.
A robust cyber governance, risk, and compliance (Cyber GRC) program is now more important than ever. At the same time, the overarching enterprise risk management strategy must be agile and scalable enough to address emerging risks and new threats to the enterprise as they occur. Understanding 2023’s cyber risk trends is important for businesses to prepare for and successfully navigate the ever-evolving risk landscape in 2024.
MetricStream remains committed to helping enterprises effectively navigate cyber risk amidst disruption and instability. Based on our interactions with customers, security leaders, industry leaders, and market research, we have collated the top 7 cyber risk trends that can help shape your risk management strategy in 2024.
What’s Next in 2024?
Artificial intelligence holds significant potential for building robust cyber risk management strategies that can address new sophisticated threats.
Enterprises are leveraging AI to build intelligent, secure, and automated systems that can detect, prevent, and even predict new attacks in real time, to help enterprises address threats immediately. From natural language processing, assisted and automated workflows, machine learning, and face detection to automatic threat detection, AI-powered cyber risk tools can equip organizations to stay on top of these emerging risks and threats in the AI era.
34 percent of organizations are already using AI security tools for risk management, while 56 percent are actively exploring AI solutions. Leveraging AI capabilities can help optimize cyber risk and IT compliance management processes with faster and more accurate insights into the control environment, automated control testing coupled with intelligent classification and remediation of issues, intent-based policy search, predictive and remedial analytics, scenario simulation, and much more. And all this is just the tip of the iceberg as the true potential of AI will unravel over the coming years. As the risk landscape continues to grow in complexity, AI-powered risk management tools will be indispensable for identifying and mitigating new-age threats.
Cyber risk quantification and assessment methods help organizations evaluate monetary risk exposure, and effectively communicate the risks, so that the C-suite can make informed business decisions. However, the methodology so far has been largely centered around the scenario-based approach, which is not only unrelated to real-world scenarios but also heavily reliant on extensive data entry, making it complex, not automated, and difficult to scale. As the cyber risk landscape continues to evolve, enterprises need tools that can ensure continuous accurate risk assessments and quantification.
Asset value-based risk quantification enables organizations to take an automated and continuous approach to risk assessments based on the value of the assets and the type of risks they’re exposed to. All asset values and their weighted risk exposures are considered to arrive at a standardized, actionable risk score that can be used to easily prioritize risks.
This approach offers the flexibility to change risk factors for more accurate and optimized decision-making. The weightage assigned to a risk can be changed based on the changing business landscape and needs. The scoring methodology is autonomous and runs continuously to incorporate data changes as risks are evaluated, which ensures accurate results. With this approach, risk managers can quickly and accurately identify which parts of the organization are exposed to critical risks and make immediate informed decisions to address the risks. Further with the introduction of AI technologies into these quantification methods, the true benefits are yet to be seen.
Alarmed at the increase of cyber threats and the impact they may have on the entire ecosystem, regulators around the world are increasingly focussing on introducing stringent regulations and laws pertaining to cyber risk management and security. This appears to be a new trend of issuing direct regulations focussed on cyber security and risk management, instead of the erstwhile practice of issuing guidelines and letting enterprises implement risk management programs as per their internal strategies.
Most of the regulations being implemented require enterprises to implement robust risk management programs and report cyber incidents, risk management practices, and management expertise in place. This includes recent regulations like SEC cybersecurity rules for public companies in the U.S., the Digital Personal Data Protection Act in India, and the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and Cyber Resilience Act in the EU.
Keeping up with changing regulatory requirements without an automated and robust compliance platform can be difficult for organizations, some of whom run the risk of unwittingly failing to comply with a new legislation or regulation. Going forward, we expect to see growing adoption of software solutions that offer automated capabilities for regulatory horizon scanning, regulatory change management, control creation from regulations, continuous control monitoring, and control testing and evidence collection.
We expect to see growing adoption of such tools across industries, enabling organizations to continuously improve cyber risk and compliance posture and significantly reduce audit costs.
Technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace today. And while there is no doubt that technology is a powerful force for good, it is also undeniable that the same technology can be used by bad actors to launch increasingly sophisticated attacks on enterprises. The emergence of generative AI in 2023 has upped enterprise cyber risk considerably.
Generative AI tools are already being used for phishing, identifying and exploiting IoT vulnerabilities, deepfakes, keystroke monitoring, malware, and ransomware. Advanced persistent threats and ransomware will also continue to be major cybersecurity issues. Attackers are using AI to analyze attack strategies before launching them and to increase the scale and speed of attacks. And they are using AI to evade existing security strategies and evade algorithms that detect suspicious activity. Such spoofing attempts are only going to evolve further.
Automated, AI-powered cyber risk management solutions are a business imperative today as the use of AI for malicious purposes will only increase in the future.
More and more organizations are required to work with third-party vendors and manage external supply chains. As risks grow increasingly interconnected, they must extend cyber risk management strategies to third-party partners and supply chains as well. According to the 2022 Ponemon Institute State of Cybersecurity and Third-Party Remote Access Security Report, 49% of surveyed organizations said that they experienced third-party cyber attacks in the past year compared to 44% in the previous 12 months.
Cyber adversaries will continue to focus on exploiting supply chain vulnerabilities in 2024 by using new and powerful technologies and methods. Inadequate risk management and security strategies, lack of encryption, open-source software, vendor applications and software with inadequate security measures, and an exponential increase in AI-based malware pose significant risks to enterprises. Cyber criminals are likely to exploit the gaps in the connection network between suppliers, and service providers. Organizations must focus on managing third-party risks to improve their overall security posture and this need is continuously increasing as all IT systems have third-party components.
The aim of a third-party cyber risk management strategy is to recognize and address the business, operational, and cyber risks linked to third parties, and subsequent parties, including fourth parties and beyond. Enterprises need to ensure stringent scrutiny of third-party suppliers and implement robust third-party cyber risk assessments to protect themselves.
Organizational spending on cyber security and risk management was expected to touch USD 188. 1 billion in 2023. This is expected to increase by 14.3 percent to reach USD 215 billion in 2024 as organizations continue to recognize the increasing risk and costs of cyber-attacks. The key areas of investment include:
Cloud security: The cloud is the foundation for any digital transformation journey and most organizations are moving their data and applications to the cloud –private, public, and hybrid. While cloud adoption is critical for innovation, scalability, and agility, it is also susceptible to cyber attacks and data breaches. There is an upswing in investment in cloud security solutions such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), and cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools. This is expected to continue in 2024.
AI and ML: Enterprise cyber security strategies in the age of AI must include AI and ML-based solutions to fortify cyber defense. These technologies improve real-time detection and response to threats and are a critical investment at a time when cyber criminals are increasingly leveraging technology to launch sophisticated attacks. Investments in AI-powered security solutions, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat intelligence, and incident response automation, are likely to grow in 2024.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security: IoT devices are increasingly becoming ubiquitous across industries. And securing them is now a business imperative. Investments in IoT security solutions, such as device authentication, encryption, and segmentation, are expected to rise.
DevSecOps: The integration of security into DevOps practices, known as DevSecOps, is gaining traction. Investments in DevSecOps tools and services, such as container security, infrastructure as code (IaC), and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR), are anticipated to increase.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Workloads on the cloud are growing at unprecedented rates, generative AI is making further inroads into enterprise digital strategy and the number of IoT devices is increasing exponentially. Identity and access management is a crucial element of enterprise risk management strategies in this hyper-connected landscape. Investments in IAM solutions, such as identity governance, administration, and privileged access management (PAM), are expected to continue growing.
Endpoint Security: Hybrid working is here to stay resulting in a highly distributed enterprise IT with multiple endpoints, which is a popular attack vector for cybercriminals. Investments in endpoint security solutions, such as endpoint detection and response will continue to increase over the next year.
Integrated risk management (IRM): Technology has created a world that is more connected than ever before. Enterprise cyber risks and vulnerabilities cannot be assessed or mitigated effectively in isolation. Most organizations now consider IRM to be foundational to their cyber risk management strategy as it combines the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks along with managing and monitoring them. 2024 will see continuing investments in IRM solutions.
Cyber security insurance: Organizations are now operating in a significantly heightened risk environment. As a result, cyber risk insurance premiums are on the rise. Annual cyber insurance premiums are currently around USD 5 billion and this is expected to increase by 20- 30 percent year on year.
Human error, callousness, and malintent remain the biggest reasons for any data breach. 74 percent of all data breaches in 2023 were directly or indirectly caused by internal personnel. Some were phishing or social engineering attacks, while others were caused by human errors or misuse.
Organizations must invest in creating a risk-aware culture through more frequent training and practical evaluations. This is not just within their own walls, but at their third-party vendors as well. Continuous training and awareness sessions are critical. It is equally important to equip the first line of defense with the skills and tools they need to identify, evaluate, and address cyber risk.
MetricStream CyberGRC enables organizations to proactively manage cyber risk and compliance with a comprehensive IT and Cyber Risk Compliance Framework that is aligned with established security standards.
With this framework, enterprises can manage IT and cyber risks more effectively, ensure compliance with all relevant regulations, manage third-party risks, and pass IT audits quickly. Organizations can also gain comprehensive insights into their overall IT risk and compliance landscape and secure the support of the leadership team by quantifying risk in business terms. They can leverage readily available industry benchmarks and rules such as ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and NIST SP800-53 to quickly connect rules to IT controls and policy exceptions.









