Introduction
Organizations often aim for different levels of scalability. As they expand, they encounter increased operational complexity, larger customer bases, and more extensive data processing needs. This growth introduces higher levels of risk, necessitating effective data management, adherence to data subject rights, and robust protection against internal and external threats.
Many organizations turn to Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) to navigate these challenges successfully.
Key Takeaways
- ERM Implementation is the process of establishing a structured approach to managing risks within an organization. This involves creating an ERM program, identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing strategies to mitigate or avoid them.
- Challenges: The common obstacles to enterprise risk management implementation include lack of executive support, cultural resistance, data silos, resource constraints, and inadequate risk awareness.
- Steps for ERM Implementation: The steps to establish a solid ERM framework include gaining executive buy-in, forming a dedicated team, conducting risk identification and assessment, planning risk responses, integrating ERM with business processes, and ensuring ongoing monitoring and reporting.
What is ERM Implementation?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) implementation is a systematic process used by organizations to identify, assess, prioritize, and mitigate all types of risks they may encounter. These risks can be financial, operational, strategic, or reputational. By implementing an ERM framework, organizations gain a holistic view of their risk landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and ensure business continuity.
Implementing ERM involves integrating risk management into every aspect of the organization, from the highest strategic level to daily operational activities. This structured approach ensures that risk management is not an isolated function but an integral part of the organization's overall strategy.
Challenges of ERM Implementation
The common challenges to implementing Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) include a lack of executive support, cultural resistance, data silos, resource constraints, and inadequate risk awareness - all factors that hinder comprehensive risk assessments.
Here are some common obstacles organizations face during ERM implementation:
Lack of Executive Buy-In:
Effective ERM requires support and commitment from the top. Without executive buy-in, risk management initiatives often fail to gain the necessary traction and resources. Ensuring that leadership understands the value and criticality of ERM is essential.
Cultural Resistance:
Risk management is a cultural shift that requires changing the mindset and behaviors of employees at all levels. Resistance to change can hinder the adoption of ERM practices. Overcoming this requires ongoing education and communication to instill a risk-aware culture.
Data Silos:
Organizations often operate in silos, with disparate departments managing their risks independently. This fragmentation leads to incomplete risk assessments and missed opportunities for cross-functional risk mitigation.
Resource Constraints:
Implementing ERM can be resource-intensive, requiring dedicated personnel, technology, and time. Organizations with limited resources may need help to allocate the necessary investments. Prioritizing ERM initiatives and demonstrating their ROI can help secure the needed resources.
Inadequate Risk Awareness:
For ERM to be effective, all employees need to be aware of the risks relevant to their roles and the organization as a whole. However, many organizations struggle with disseminating risk information and ensuring that everyone understands their role in risk management. Comprehensive training and clear communication channels are essential to build risk awareness.
How to Implement Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Here’s how you can systematically implement ERM in your organization:
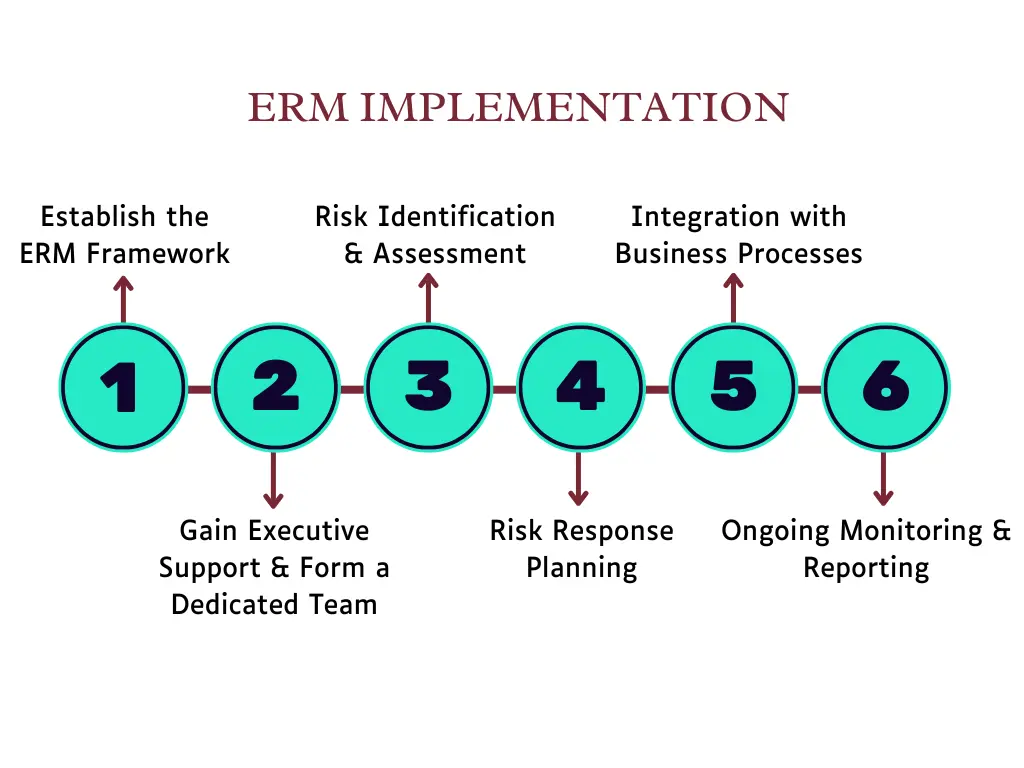
Establish the ERM Framework
Begin by setting a solid foundation with a robust ERM framework. This includes:
- Defining the Scope and Objectives: Identify the specific goals of your ERM program. What kind of risks are you looking to manage (for example: financial risks, operational risks, etc.? Establish clear objectives that align with your organization’s strategic goals.
- Choosing an ERM Framework: Select an industry-standard framework such as COSO ERM or ISO 31000. These frameworks offer structured approaches and guidelines that can be customized to fit your organization’s unique needs.
Gain Executive Support and Form a Dedicated Team
Secure buy-in from top executives and the board of directors. Their support is crucial for allocating resources and enforcing the ERM policies across all levels of the organization.
Form a cross-functional team consisting of risk management professionals, key stakeholders, and representatives from various departments.
Risk Identification and Assessment
Conduct workshops, interviews, and surveys to gather input from employees and stakeholders. Utilize tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to capture a comprehensive list of risks. Evaluate the identified risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. Techniques such as risk matrices, heat maps, and quantitative risk assessment models can be useful for prioritizing risks.
Risk Response Planning
Decide on the best course of action for each risk—whether to avoid, mitigate, transfer, or accept it. For example, financial risks might be mitigated through hedging strategies, while operational risks might be addressed through process improvements.
Integration with Business Processes
Ensure that risk management considerations are integrated into your strategic planning and decision-making processes. This helps in aligning risk management with the organization’s goals.
Remember to incorporate risk management activities into everyday business processes as well. This can be achieved by integrating risk assessment criteria into project management frameworks, procurement processes, and other operational workflows.
Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting
Establish key risk indicators (KRIs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor risks and the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies continuously. Regular audits and reviews should be conducted to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
These reports should be regularly shared with executives, the board, and other relevant parties to facilitate informed decision-making.
Challenges of ERM Implementation
While ERM frameworks offer significant advantages, it’s important to understand the limitations and pitfalls associated with their implementation. These drawbacks do not negate the value of ERM but highlight areas that require careful consideration and continuous improvement.
1. Complexity and Resource Intensity
ERM frameworks can be complex to design and implement, especially in large organizations. They often require significant time, financial investment, and human resources. For small and mid-sized companies, the cost and effort associated with a full-scale ERM program may outweigh the perceived benefits.
2. Over-Reliance on Quantitative Methods
While quantitative tools are valuable in assessing risks, an over-reliance on numerical data can lead to blind spots. Some risks—like reputational damage or strategic shifts—are difficult to quantify but can have significant impacts. A balanced approach that includes qualitative analysis is crucial for a holistic view.
3. False Sense of Security
Implementing ERM can sometimes create a false sense of security, leading stakeholders to believe that all risks are fully managed. This complacency can be dangerous, as it may reduce vigilance and discourage adaptive thinking, especially in dynamic or uncertain environments.
4. Bureaucratic Burden
ERM frameworks can introduce additional layers of bureaucracy, slowing down decision-making processes. If not carefully managed, the administrative aspects of ERM may hinder agility and innovation within the organization, particularly in fast-paced industries.
5. Misalignment with Strategic Objectives
If ERM activities are not closely aligned with business goals, they risk becoming siloed or redundant. Risk assessments must be integrated into strategic planning to ensure that risk management supports—not obstructs—organizational growth and competitiveness.
6. Limited Flexibility
Some ERM frameworks are rigid in structure, making it difficult to adapt to emerging risks or changes in the business environment. Flexibility is essential for organizations to remain resilient and responsive to new challenges and opportunities.
7. Cultural Barriers
ERM success depends heavily on organizational culture. In environments where transparency, accountability, and risk awareness are lacking, ERM frameworks may fail to gain traction. Changing culture is a long-term endeavor that requires sustained leadership effort.
Recognizing these limitations allows organizations to address them proactively and refine their ERM strategies. By maintaining flexibility, aligning with strategic goals, and fostering a risk-aware culture, businesses can enhance the effectiveness of their ERM efforts.
ERM Implementation Best Practices
To ensure the successful adoption of ERM, organizations must follow structured best practices that promote efficiency, consistency, and long-term sustainability. Below are key best practices that can help businesses implement ERM effectively:
1. Secure Executive Sponsorship
ERM implementation starts at the top. Senior leadership must champion ERM efforts by setting clear expectations, providing necessary resources, and fostering a risk-aware culture. When executives actively support ERM, it encourages organization-wide adoption and ensures alignment with business objectives.
2. Establish a Clear Risk Management Framework
A well-defined ERM framework provides the structure needed to assess, monitor, and mitigate risks. Organizations should establish clear policies, risk governance models, and risk appetite statements that outline how risks will be managed across different levels.
3. Foster a Risk-Aware Culture
An ERM program is only as strong as the people executing it. Businesses must promote a risk-aware culture by educating employees about their role in risk management. This includes conducting regular training sessions, encouraging open discussions about risks, and reinforcing the importance of proactive risk identification.
4. Implement a Centralized Risk Register
Maintaining a centralized risk register helps organizations document, track, and analyze risks in a structured manner. A well-maintained risk register allows businesses to identify patterns, measure risk impact, and take proactive action before issues escalate.
5. Integrate ERM into Business Strategy
ERM should not function in isolation. It should be embedded into strategic planning, decision-making, and operational processes. Organizations that integrate risk management with business objectives can better anticipate challenges and seize opportunities while maintaining stability.
6. Leverage Technology for Risk Monitoring
Modern risk management tools and software help businesses track risks in real time, automate reporting, and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Investing in the right technology enhances efficiency and provides better insights into the risk landscape.
7. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments and Scenario Planning
Periodic risk assessments help organizations stay ahead of potential threats. Scenario planning and stress testing enable businesses to evaluate different risk scenarios and prepare response strategies, ensuring resilience in the face of uncertainty.
8. Develop a Clear Communication Strategy
Transparent communication is critical for ERM success. Risk information should be communicated across all levels of the organization, ensuring that key stakeholders are aware of risks, mitigation strategies, and changes in risk profiles. Regular reporting to executives and board members helps maintain accountability.
9. Establish Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) provide measurable data points that help organizations track risk exposure. Establishing relevant KRIs allows businesses to monitor risks effectively and take timely corrective action when thresholds are exceeded.
10. Continuously Improve the ERM Program
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and refinement. Organizations should regularly review their ERM framework, analyze past risk events, and update their approach based on lessons learned and emerging risks.
By following these best practices, organizations can build a strong ERM framework that enhances resilience, improves decision-making, and drives long-term success. Implementing ERM effectively not only mitigates risks but also creates opportunities for sustainable growth.
ERM Implementation Case Study
Enhancing Performance through Unified ERM: A Global Consulting and IT Services Leader
A global leader in consulting and IT services, tasked with managing an immense portfolio of 10,000 accounts and 60,000 projects globally, faced substantial challenges in aligning their risk management strategy with their strategic goals. The company's traditional risk assessment processes were manual and siloed, resulting in delays and inefficiencies that hampered the timely reporting of critical risk information. This fragmentation made it difficult to evaluate risks and also obstructed their ability to connect risk impacts to overall business performance objectives effectively.
The company turned to MetricStream Enterprise Risk Management to overhaul its risk management strategy along with audit management, and SOX compliance. With MetricStream products project owners could identify and map risks directly to their business performance objectives and strategic goals. This integration allowed stakeholders to gain a holistic view of how various risks could influence revenue, performance, and operational costs, thereby enhancing decision-making processes. By linking audit findings with ERM, the company achieved improved insights into project health and more efficient audit processes.
The implementation of MetricStream's solution has addressed their immediate challenges and fortified their risk management framework, aligning it closely with their long-term strategic objectives.
Elevating Risk Management Maturity: An International Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Conglomerate
A global pharmaceutical and healthcare conglomerate, managing over 250 companies across various divisions and employing 125,000 individuals worldwide, faced significant challenges in coordinating its risk management processes. The company’s existing setup was plagued by fragmented risk management processes, multiple disparate data systems, and an inconsistent GRC taxonomy. These issues obstructed their visibility into emerging risks and complicated their efforts to standardize policies and controls across the enterprise.
In their quest to elevate their risk management maturity, the conglomerate adopted MetricStream’s Enterprise Risk Management system. This robust solution enabled the company to harmonize risk management processes by providing a unified GRC taxonomy and greater visibility into emerging risks. Supporting 400 users across 1,200 suppliers, MetricStream's solution offered a centralized view of risks and seamlessly integrated control test results and audit schedules. The comprehensive ERM solution has significantly enhanced the company’s ability to aggregate and normalize risk data, thus improving risk reporting and fostering a culture of risk awareness. With real-time insights into risk management, the conglomerate can now make faster, more informed decisions, significantly strengthening its overall GRC posture.
Conclusion
ERM implementation is an evolving process that requires sustained effort and adaptation. As organizations grow and change, so do the risks they face. A successful ERM implementation hinges on a clear strategy, committed leadership, continuous engagement, and the integration of robust technological solutions
The right software can streamline risk management processes, provide real-time insights, and facilitate better decision-making. MetricStream’s Enterprise Risk Management solutions offer a comprehensive suite of tools designed to support every aspect of ERM. We stand ready to assist you in this crucial endeavor, offering the tools and expertise necessary to build a resilient and risk-aware organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a structured process that helps organizations identify, assess, prioritize, and mitigate various risks. By integrating ERM into all business functions, organizations can improve decision-making, protect assets, and ensure business continuity. Common ERM frameworks include COSO and ISO 31000.
What types of risks should ERM address?
ERM should address a wide range of risks, including financial, operational, strategic, compliance, and reputational risks. By considering various risk categories, organizations can comprehensively safeguard their assets and objectives.
What are the key components of the COSO ERM Framework?
The COSO ERM Framework consists of five interrelated components: Governance and Culture, Strategy and Objective-Setting, Performance, Review and Revision, and Information, Communication, and Reporting.
Organizations often aim for different levels of scalability. As they expand, they encounter increased operational complexity, larger customer bases, and more extensive data processing needs. This growth introduces higher levels of risk, necessitating effective data management, adherence to data subject rights, and robust protection against internal and external threats.
Many organizations turn to Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) to navigate these challenges successfully.
- ERM Implementation is the process of establishing a structured approach to managing risks within an organization. This involves creating an ERM program, identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing strategies to mitigate or avoid them.
- Challenges: The common obstacles to enterprise risk management implementation include lack of executive support, cultural resistance, data silos, resource constraints, and inadequate risk awareness.
- Steps for ERM Implementation: The steps to establish a solid ERM framework include gaining executive buy-in, forming a dedicated team, conducting risk identification and assessment, planning risk responses, integrating ERM with business processes, and ensuring ongoing monitoring and reporting.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) implementation is a systematic process used by organizations to identify, assess, prioritize, and mitigate all types of risks they may encounter. These risks can be financial, operational, strategic, or reputational. By implementing an ERM framework, organizations gain a holistic view of their risk landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and ensure business continuity.
Implementing ERM involves integrating risk management into every aspect of the organization, from the highest strategic level to daily operational activities. This structured approach ensures that risk management is not an isolated function but an integral part of the organization's overall strategy.
The common challenges to implementing Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) include a lack of executive support, cultural resistance, data silos, resource constraints, and inadequate risk awareness - all factors that hinder comprehensive risk assessments.
Here are some common obstacles organizations face during ERM implementation:
Lack of Executive Buy-In:
Effective ERM requires support and commitment from the top. Without executive buy-in, risk management initiatives often fail to gain the necessary traction and resources. Ensuring that leadership understands the value and criticality of ERM is essential.
Cultural Resistance:
Risk management is a cultural shift that requires changing the mindset and behaviors of employees at all levels. Resistance to change can hinder the adoption of ERM practices. Overcoming this requires ongoing education and communication to instill a risk-aware culture.
Data Silos:
Organizations often operate in silos, with disparate departments managing their risks independently. This fragmentation leads to incomplete risk assessments and missed opportunities for cross-functional risk mitigation.
Resource Constraints:
Implementing ERM can be resource-intensive, requiring dedicated personnel, technology, and time. Organizations with limited resources may need help to allocate the necessary investments. Prioritizing ERM initiatives and demonstrating their ROI can help secure the needed resources.
Inadequate Risk Awareness:
For ERM to be effective, all employees need to be aware of the risks relevant to their roles and the organization as a whole. However, many organizations struggle with disseminating risk information and ensuring that everyone understands their role in risk management. Comprehensive training and clear communication channels are essential to build risk awareness.
Here’s how you can systematically implement ERM in your organization:

Establish the ERM Framework
Begin by setting a solid foundation with a robust ERM framework. This includes:
- Defining the Scope and Objectives: Identify the specific goals of your ERM program. What kind of risks are you looking to manage (for example: financial risks, operational risks, etc.? Establish clear objectives that align with your organization’s strategic goals.
- Choosing an ERM Framework: Select an industry-standard framework such as COSO ERM or ISO 31000. These frameworks offer structured approaches and guidelines that can be customized to fit your organization’s unique needs.
Gain Executive Support and Form a Dedicated Team
Secure buy-in from top executives and the board of directors. Their support is crucial for allocating resources and enforcing the ERM policies across all levels of the organization.
Form a cross-functional team consisting of risk management professionals, key stakeholders, and representatives from various departments.
Risk Identification and Assessment
Conduct workshops, interviews, and surveys to gather input from employees and stakeholders. Utilize tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to capture a comprehensive list of risks. Evaluate the identified risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. Techniques such as risk matrices, heat maps, and quantitative risk assessment models can be useful for prioritizing risks.
Risk Response Planning
Decide on the best course of action for each risk—whether to avoid, mitigate, transfer, or accept it. For example, financial risks might be mitigated through hedging strategies, while operational risks might be addressed through process improvements.
Integration with Business Processes
Ensure that risk management considerations are integrated into your strategic planning and decision-making processes. This helps in aligning risk management with the organization’s goals.
Remember to incorporate risk management activities into everyday business processes as well. This can be achieved by integrating risk assessment criteria into project management frameworks, procurement processes, and other operational workflows.
Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting
Establish key risk indicators (KRIs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor risks and the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies continuously. Regular audits and reviews should be conducted to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
These reports should be regularly shared with executives, the board, and other relevant parties to facilitate informed decision-making.
While ERM frameworks offer significant advantages, it’s important to understand the limitations and pitfalls associated with their implementation. These drawbacks do not negate the value of ERM but highlight areas that require careful consideration and continuous improvement.
1. Complexity and Resource Intensity
ERM frameworks can be complex to design and implement, especially in large organizations. They often require significant time, financial investment, and human resources. For small and mid-sized companies, the cost and effort associated with a full-scale ERM program may outweigh the perceived benefits.
2. Over-Reliance on Quantitative Methods
While quantitative tools are valuable in assessing risks, an over-reliance on numerical data can lead to blind spots. Some risks—like reputational damage or strategic shifts—are difficult to quantify but can have significant impacts. A balanced approach that includes qualitative analysis is crucial for a holistic view.
3. False Sense of Security
Implementing ERM can sometimes create a false sense of security, leading stakeholders to believe that all risks are fully managed. This complacency can be dangerous, as it may reduce vigilance and discourage adaptive thinking, especially in dynamic or uncertain environments.
4. Bureaucratic Burden
ERM frameworks can introduce additional layers of bureaucracy, slowing down decision-making processes. If not carefully managed, the administrative aspects of ERM may hinder agility and innovation within the organization, particularly in fast-paced industries.
5. Misalignment with Strategic Objectives
If ERM activities are not closely aligned with business goals, they risk becoming siloed or redundant. Risk assessments must be integrated into strategic planning to ensure that risk management supports—not obstructs—organizational growth and competitiveness.
6. Limited Flexibility
Some ERM frameworks are rigid in structure, making it difficult to adapt to emerging risks or changes in the business environment. Flexibility is essential for organizations to remain resilient and responsive to new challenges and opportunities.
7. Cultural Barriers
ERM success depends heavily on organizational culture. In environments where transparency, accountability, and risk awareness are lacking, ERM frameworks may fail to gain traction. Changing culture is a long-term endeavor that requires sustained leadership effort.
Recognizing these limitations allows organizations to address them proactively and refine their ERM strategies. By maintaining flexibility, aligning with strategic goals, and fostering a risk-aware culture, businesses can enhance the effectiveness of their ERM efforts.
To ensure the successful adoption of ERM, organizations must follow structured best practices that promote efficiency, consistency, and long-term sustainability. Below are key best practices that can help businesses implement ERM effectively:
1. Secure Executive Sponsorship
ERM implementation starts at the top. Senior leadership must champion ERM efforts by setting clear expectations, providing necessary resources, and fostering a risk-aware culture. When executives actively support ERM, it encourages organization-wide adoption and ensures alignment with business objectives.
2. Establish a Clear Risk Management Framework
A well-defined ERM framework provides the structure needed to assess, monitor, and mitigate risks. Organizations should establish clear policies, risk governance models, and risk appetite statements that outline how risks will be managed across different levels.
3. Foster a Risk-Aware Culture
An ERM program is only as strong as the people executing it. Businesses must promote a risk-aware culture by educating employees about their role in risk management. This includes conducting regular training sessions, encouraging open discussions about risks, and reinforcing the importance of proactive risk identification.
4. Implement a Centralized Risk Register
Maintaining a centralized risk register helps organizations document, track, and analyze risks in a structured manner. A well-maintained risk register allows businesses to identify patterns, measure risk impact, and take proactive action before issues escalate.
5. Integrate ERM into Business Strategy
ERM should not function in isolation. It should be embedded into strategic planning, decision-making, and operational processes. Organizations that integrate risk management with business objectives can better anticipate challenges and seize opportunities while maintaining stability.
6. Leverage Technology for Risk Monitoring
Modern risk management tools and software help businesses track risks in real time, automate reporting, and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Investing in the right technology enhances efficiency and provides better insights into the risk landscape.
7. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments and Scenario Planning
Periodic risk assessments help organizations stay ahead of potential threats. Scenario planning and stress testing enable businesses to evaluate different risk scenarios and prepare response strategies, ensuring resilience in the face of uncertainty.
8. Develop a Clear Communication Strategy
Transparent communication is critical for ERM success. Risk information should be communicated across all levels of the organization, ensuring that key stakeholders are aware of risks, mitigation strategies, and changes in risk profiles. Regular reporting to executives and board members helps maintain accountability.
9. Establish Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) provide measurable data points that help organizations track risk exposure. Establishing relevant KRIs allows businesses to monitor risks effectively and take timely corrective action when thresholds are exceeded.
10. Continuously Improve the ERM Program
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation and refinement. Organizations should regularly review their ERM framework, analyze past risk events, and update their approach based on lessons learned and emerging risks.
By following these best practices, organizations can build a strong ERM framework that enhances resilience, improves decision-making, and drives long-term success. Implementing ERM effectively not only mitigates risks but also creates opportunities for sustainable growth.
Enhancing Performance through Unified ERM: A Global Consulting and IT Services Leader
A global leader in consulting and IT services, tasked with managing an immense portfolio of 10,000 accounts and 60,000 projects globally, faced substantial challenges in aligning their risk management strategy with their strategic goals. The company's traditional risk assessment processes were manual and siloed, resulting in delays and inefficiencies that hampered the timely reporting of critical risk information. This fragmentation made it difficult to evaluate risks and also obstructed their ability to connect risk impacts to overall business performance objectives effectively.
The company turned to MetricStream Enterprise Risk Management to overhaul its risk management strategy along with audit management, and SOX compliance. With MetricStream products project owners could identify and map risks directly to their business performance objectives and strategic goals. This integration allowed stakeholders to gain a holistic view of how various risks could influence revenue, performance, and operational costs, thereby enhancing decision-making processes. By linking audit findings with ERM, the company achieved improved insights into project health and more efficient audit processes.
The implementation of MetricStream's solution has addressed their immediate challenges and fortified their risk management framework, aligning it closely with their long-term strategic objectives.
Elevating Risk Management Maturity: An International Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Conglomerate
A global pharmaceutical and healthcare conglomerate, managing over 250 companies across various divisions and employing 125,000 individuals worldwide, faced significant challenges in coordinating its risk management processes. The company’s existing setup was plagued by fragmented risk management processes, multiple disparate data systems, and an inconsistent GRC taxonomy. These issues obstructed their visibility into emerging risks and complicated their efforts to standardize policies and controls across the enterprise.
In their quest to elevate their risk management maturity, the conglomerate adopted MetricStream’s Enterprise Risk Management system. This robust solution enabled the company to harmonize risk management processes by providing a unified GRC taxonomy and greater visibility into emerging risks. Supporting 400 users across 1,200 suppliers, MetricStream's solution offered a centralized view of risks and seamlessly integrated control test results and audit schedules. The comprehensive ERM solution has significantly enhanced the company’s ability to aggregate and normalize risk data, thus improving risk reporting and fostering a culture of risk awareness. With real-time insights into risk management, the conglomerate can now make faster, more informed decisions, significantly strengthening its overall GRC posture.
ERM implementation is an evolving process that requires sustained effort and adaptation. As organizations grow and change, so do the risks they face. A successful ERM implementation hinges on a clear strategy, committed leadership, continuous engagement, and the integration of robust technological solutions
The right software can streamline risk management processes, provide real-time insights, and facilitate better decision-making. MetricStream’s Enterprise Risk Management solutions offer a comprehensive suite of tools designed to support every aspect of ERM. We stand ready to assist you in this crucial endeavor, offering the tools and expertise necessary to build a resilient and risk-aware organization.
What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a structured process that helps organizations identify, assess, prioritize, and mitigate various risks. By integrating ERM into all business functions, organizations can improve decision-making, protect assets, and ensure business continuity. Common ERM frameworks include COSO and ISO 31000.
What types of risks should ERM address?
ERM should address a wide range of risks, including financial, operational, strategic, compliance, and reputational risks. By considering various risk categories, organizations can comprehensively safeguard their assets and objectives.
What are the key components of the COSO ERM Framework?
The COSO ERM Framework consists of five interrelated components: Governance and Culture, Strategy and Objective-Setting, Performance, Review and Revision, and Information, Communication, and Reporting.








