Introduction
In an age where business dynamics are continually shifting and the global market is becoming more interconnected, the importance of operational risk management (ORM) cannot be overstated. At its core, ORM is about anticipating, identifying, and managing the risks that could potentially hinder financial services organizations’ operations, reputation, and profitability. The essence of ORM lies not just in averting financial losses but in preserving the corporate integrity and trust that organizations spend years building.
As businesses evolve, so does the landscape of operational risks. From cyber threats and data breaches to supply chain disruptions, IT failure, and regulatory compliance issues, the spectrum of risks is vast and continuously changing. This fluid landscape necessitates the adoption of sophisticated ORM tools, making them no longer just advantageous but essential for businesses aiming to navigate the intricacies of modern-day risks.
Key Takeaways
- ORM tools help organizations identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate risks associated with their operations, enhancing visibility and decision-making.
- Consider capabilities such as built-in support for industry frameworks, scalability, reporting capabilities, ease of configuration, integration with existing systems, user-friendliness, and vendor support when choosing an ORM tool.
- Implementing ORM tools improves risk visibility, decision-making, operational resilience, compliance with regulations, and overall efficiency.
- Implementing an ORM tool requires following several steps, including defining a clear Statement of Work (SOW), ensuring accurate data migration and integration, providing comprehensive training, managing project risks, and continuously optimizing the tool with vendor support.
What is an ORM Tool?
An operational risk management (ORM) tool is a specialized software solution designed to help organizations identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate risks associated with their operational processes. By leveraging advanced analytics and well-defined workflows, ORM tools facilitate the systematic management of risks that could potentially disrupt business operations, impact financial performance, or harm an organization’s reputation.
Selecting the Right ORM Tool
Think of these factors as the necessary ingredients for an effective ORM solution.
Industry Frameworks and Best Practices
The tool should enable organizations to align their ORM program to industry frameworks and best practices. This includes capabilities and functionalities such as a centralized risk and control library, well-defined risk and control self-assessment (RCSA) workflows, loss management as per industry regulations like the Basel Accords, systematic issue and action management, and more.
Scalability and Adaptability
Look for a tool that can handle increasing data volumes and complexity over time, as your processes and risks evolve. A solution that offers modules to address specific areas like vendor or cyber risk demonstrates adaptability. As new impacts come into effect, the tool should be able to pivot quickly.
Reporting and Visualization
Data is useless without the ability to analyze it and gain insights. Look for tools with robust reporting features that provide an at-a-glance view of your risk indicators through interactive dashboards and visuals.
Easy Configuration and Personalization
A tool that allows for flexible configuration ensures that it can be tailored to align with unique business processes and risk management frameworks. This adaptability can significantly reduce the time and effort required to implement and maintain the tool.
Seamless Integration with External Systems
With organizations increasingly depending on external systems to streamline and accelerate their processes, pull relevant information for better-informed decision-making, and take a comprehensive approach to the bigger picture, integration capabilities have become extremely important. An effective ORM tool should seamlessly integrate with your existing external systems, such as ERP, CRM, and other enterprise software.
Easy to Use and Intuitive
Choose an ORM tool that is user-friendly and intuitive. The easier it is for your team to navigate and use the tool, the quicker they can adopt it and leverage its full potential. A complicated interface can hinder productivity and can possibly lead to user frustration.
Strong Roadmap and Innovation Strategy Alignment
Ensure that the ORM solution provider has a robust innovation strategy and a product roadmap that aligns with your company’s goals and objectives. A forward-thinking provider will continually evolve their tool to meet emerging risk management needs, ensuring long-term relevance and value.
User groups
Consider whether the ORM solution provider has established user groups such as product councils, customer councils, and special interest groups. These forums are valuable for knowledge sharing, gaining product feedback, and staying updated on best practices.
Cost and Implementation
Solutions vary widely in pricing models and implementation requirements. Evaluate your budget, resources, and timeline to choose a tool that you can implement successfully.
Benefits of Implementing ORM Tool
Implementing a robust ORM tool can enable organizations to effectively streamline processes, enhance visibility, and reduce risks. With technology and human expertise working together, comprehensive, these software solutions can help organizations switch from reactive to proactive strategy and spend more time on high-value activities that safeguard the organization.
Here are some of the main benefits of adopting and implementing an ORM tool:
Improved Risk Visibility and Understanding
Adopting a robust ORM tool illuminates the hidden corners and brings into sharp focus the contours of operational risks. This enhanced visibility is all about understanding them in a nuanced manner, appreciating their potential impact, and recognizing their interconnections.
By shedding light on the risk landscape, organizations can navigate it with greater confidence, making informed decisions that are rooted in clarity rather than conjecture.
Enhanced Decision-Making and Resource Allocation
This flows naturally from this increased visibility. With a clear grasp of the operational risks, businesses can prioritize risks effectively, directing resources and attention to areas where they are needed most.
This strategic allocation optimizes the use of limited resources, maximizing return on investment and steering the organization towards its objectives with calculated precision.
Powering Resilience with Accurate and Timely Risk Insights
The ultimate test of an organization's mettle lies in its ability to weather storms and emerge unscathed—or even stronger. ORM tools are pivotal in building this resilience, equipping businesses with the strategies and insights needed to maintain continuity amidst crises. As the world becomes increasingly unpredictable, operational resilience evolves from a competitive edge to a fundamental necessity,
Compliance with Industry Regulations and Frameworks
ORM tools assist organizations in maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as the Basel Accords, by providing frameworks, controls, and monitoring capabilities. By automating compliance processes, documenting controls, and tracking regulatory changes, these tools help organizations demonstrate adherence to compliance obligations and enhance overall governance practices.
Competitive Advantage
By efficiently managing operational risks, you can improve decision-making, enhance compliance, and turn risks into a strategic advantage. This approach to risk management can also improve your reputation in the market, making your organization more attractive to customers, investors, and partners.
Better Efficiency
With the automation of repeatable tasks, the tool reduces the time and effort required for manual risk management activities. This frees up resources, allowing your team to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine risk management tasks. Moreover, real-time data analytics and reporting capabilities enable quicker decision-making, ensuring potential risks are addressed promptly and effectively.
How to Implement ORM Tools
Here are the key steps that organizations can follow to implement an ORM software solution:
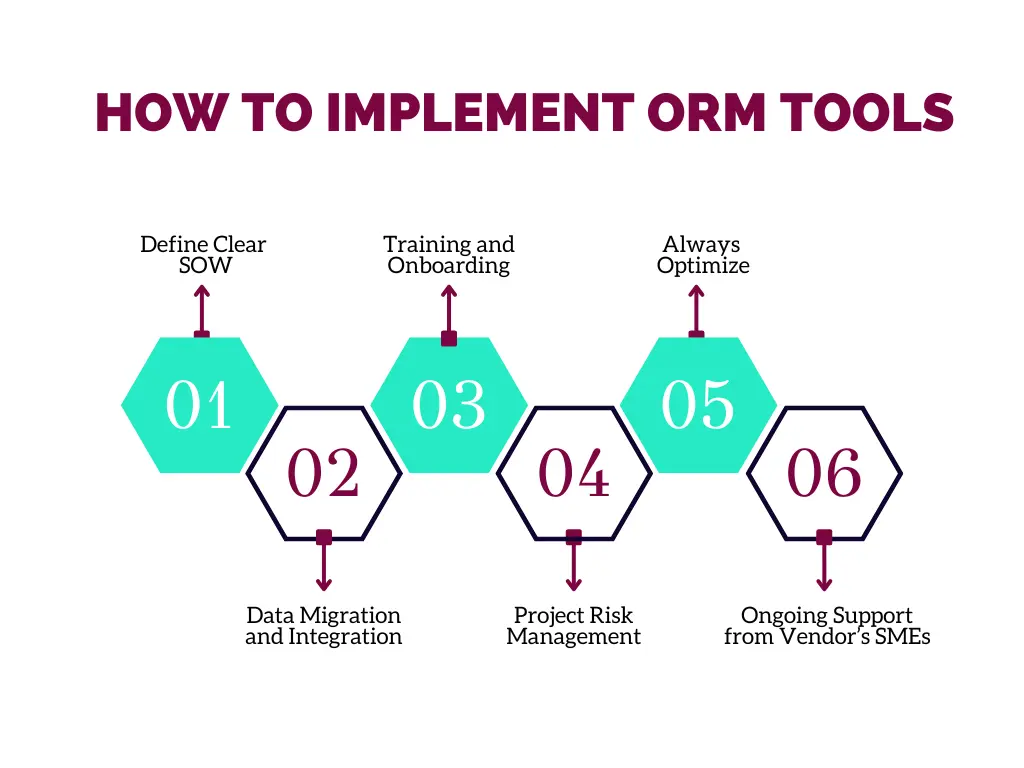
Define Clear SOW
Start by defining a clear Statement of Work (SOW). Outline the scope, including what the ORM tool will cover and what it won't. Set realistic timelines for each phase of the implementation. Assign responsibilities to team members, ensuring everyone understands their role and deliverables.
Data Migration and Integration
Ensure that all relevant data is accurately transferred to the new system. Verify the integrity and completeness of data before going live. Additionally, focus on integrating the ORM tool with existing systems to create a unified data environment.
Training and Onboarding
Don't just drop the new tool into your organization's lap and expect people to figure it out. Develop a comprehensive training program to teach employees how the tool works and their benefits. Onboard people slowly in phases so they can get used to the tool gradually.
Project Risk Management
Identify the risks to the tool’s implementation and user adoption and draw a project risk management plan. Regularly monitor the risks and address any issues promptly. Proactive risk management ensures the smooth implementation and adoption of the tool and minimizes disruptions.
Always Optimize
Once the tool is deployed, it needs to be reviewed and upgraded to ensure it is working as intended. Monitor how people use them and look for ways to enhance the user experience. Send out surveys to get feedback on what's working and not working. This feedback can then be shared with the software provider to innovate and optimize the tool, driving more user adoption.
Ongoing Support from Vendor’s SMEs
Following the initial launch and training, organizations should engage with the software providers to not just escalate issues and provide feedback on the tool but also share knowledge, expertise, and best practices with their subject matter experts (SMEs), customer and product councils, special interest groups, etc. This will help organizations continuously improve their ORM strategy and ensure that it is aligned with industry best practices.
The Future of Operational Risk Management Tools
With technology advancing at breakneck speed, ORM tools will look very different in just a few years. Some of the most promising innovations include:
- Risk modeling algorithms: AI can analyze huge volumes of data to detect complex patterns and insights humans might miss.
- Automated risk assessments: Tedious risk assessment processes like surveys, checklists, and risk rating matrices could be automated using natural language processing. AI could review policies, incident reporting, and audit findings to detect, categorize, and score risks.
- Risk visualization dashboards: Advanced data visualization tools can translate complex risk data into intuitive, interactive dashboards. These dashboards provide a holistic view of risks across the company with drill-down capabilities to analyze risks.
How MetricStream Operational Risk Management (ORM) Software Can Help
MetricStream Operational Risk Management helps organizations automate and streamline operational risk processes. It is purpose-built to meet the operational risk needs of banks and financial services institutions, including a centralized risk and control library and well-defined workflows for risk and control self-assessments, loss management, KRIs tracking, issue management, and more. Graphical dashboards and powerful reports with drill-down capabilities enable risk practitioners to gain actionable risk insights and slide and dice the data to pinpoint problem areas to address them proactively.
To learn more about MetricStream Operational Risk Management (ORM) software, request a personalized demo today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the top ORM tools of 2025?
Organizations contemplating which ORM tool to purchase can refer to the reports from independent research firms, including Chartis, Forrester, and Gartner. MetricStream has been named a Category Leader in all seven quadrants of the Chartis Research RiskTech Quadrant® for Integrated GRC Solutions, 2024, including Operational risk, Internal audit, Third-party risk, IT risk, Conduct risk and controls, GRC analytics, and Enterprise GRC. MetricStream was also recognized as a Leader in The Forrester Wave™: Governance, Risk, and Compliance Platforms, Q4 2023.
To learn more, read our blog “What It Takes to Be a Leader in Governance, Risk, and Compliance”, by Pat McParland, AVP of Product Marketing at MetricStream.
In an age where business dynamics are continually shifting and the global market is becoming more interconnected, the importance of operational risk management (ORM) cannot be overstated. At its core, ORM is about anticipating, identifying, and managing the risks that could potentially hinder financial services organizations’ operations, reputation, and profitability. The essence of ORM lies not just in averting financial losses but in preserving the corporate integrity and trust that organizations spend years building.
As businesses evolve, so does the landscape of operational risks. From cyber threats and data breaches to supply chain disruptions, IT failure, and regulatory compliance issues, the spectrum of risks is vast and continuously changing. This fluid landscape necessitates the adoption of sophisticated ORM tools, making them no longer just advantageous but essential for businesses aiming to navigate the intricacies of modern-day risks.
- ORM tools help organizations identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate risks associated with their operations, enhancing visibility and decision-making.
- Consider capabilities such as built-in support for industry frameworks, scalability, reporting capabilities, ease of configuration, integration with existing systems, user-friendliness, and vendor support when choosing an ORM tool.
- Implementing ORM tools improves risk visibility, decision-making, operational resilience, compliance with regulations, and overall efficiency.
- Implementing an ORM tool requires following several steps, including defining a clear Statement of Work (SOW), ensuring accurate data migration and integration, providing comprehensive training, managing project risks, and continuously optimizing the tool with vendor support.
An operational risk management (ORM) tool is a specialized software solution designed to help organizations identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate risks associated with their operational processes. By leveraging advanced analytics and well-defined workflows, ORM tools facilitate the systematic management of risks that could potentially disrupt business operations, impact financial performance, or harm an organization’s reputation.
Think of these factors as the necessary ingredients for an effective ORM solution.
Industry Frameworks and Best Practices
The tool should enable organizations to align their ORM program to industry frameworks and best practices. This includes capabilities and functionalities such as a centralized risk and control library, well-defined risk and control self-assessment (RCSA) workflows, loss management as per industry regulations like the Basel Accords, systematic issue and action management, and more.
Scalability and Adaptability
Look for a tool that can handle increasing data volumes and complexity over time, as your processes and risks evolve. A solution that offers modules to address specific areas like vendor or cyber risk demonstrates adaptability. As new impacts come into effect, the tool should be able to pivot quickly.
Reporting and Visualization
Data is useless without the ability to analyze it and gain insights. Look for tools with robust reporting features that provide an at-a-glance view of your risk indicators through interactive dashboards and visuals.
Easy Configuration and Personalization
A tool that allows for flexible configuration ensures that it can be tailored to align with unique business processes and risk management frameworks. This adaptability can significantly reduce the time and effort required to implement and maintain the tool.
Seamless Integration with External Systems
With organizations increasingly depending on external systems to streamline and accelerate their processes, pull relevant information for better-informed decision-making, and take a comprehensive approach to the bigger picture, integration capabilities have become extremely important. An effective ORM tool should seamlessly integrate with your existing external systems, such as ERP, CRM, and other enterprise software.
Easy to Use and Intuitive
Choose an ORM tool that is user-friendly and intuitive. The easier it is for your team to navigate and use the tool, the quicker they can adopt it and leverage its full potential. A complicated interface can hinder productivity and can possibly lead to user frustration.
Strong Roadmap and Innovation Strategy Alignment
Ensure that the ORM solution provider has a robust innovation strategy and a product roadmap that aligns with your company’s goals and objectives. A forward-thinking provider will continually evolve their tool to meet emerging risk management needs, ensuring long-term relevance and value.
User groups
Consider whether the ORM solution provider has established user groups such as product councils, customer councils, and special interest groups. These forums are valuable for knowledge sharing, gaining product feedback, and staying updated on best practices.
Cost and Implementation
Solutions vary widely in pricing models and implementation requirements. Evaluate your budget, resources, and timeline to choose a tool that you can implement successfully.
Implementing a robust ORM tool can enable organizations to effectively streamline processes, enhance visibility, and reduce risks. With technology and human expertise working together, comprehensive, these software solutions can help organizations switch from reactive to proactive strategy and spend more time on high-value activities that safeguard the organization.
Here are some of the main benefits of adopting and implementing an ORM tool:
Improved Risk Visibility and Understanding
Adopting a robust ORM tool illuminates the hidden corners and brings into sharp focus the contours of operational risks. This enhanced visibility is all about understanding them in a nuanced manner, appreciating their potential impact, and recognizing their interconnections.
By shedding light on the risk landscape, organizations can navigate it with greater confidence, making informed decisions that are rooted in clarity rather than conjecture.
Enhanced Decision-Making and Resource Allocation
This flows naturally from this increased visibility. With a clear grasp of the operational risks, businesses can prioritize risks effectively, directing resources and attention to areas where they are needed most.
This strategic allocation optimizes the use of limited resources, maximizing return on investment and steering the organization towards its objectives with calculated precision.
Powering Resilience with Accurate and Timely Risk Insights
The ultimate test of an organization's mettle lies in its ability to weather storms and emerge unscathed—or even stronger. ORM tools are pivotal in building this resilience, equipping businesses with the strategies and insights needed to maintain continuity amidst crises. As the world becomes increasingly unpredictable, operational resilience evolves from a competitive edge to a fundamental necessity,
Compliance with Industry Regulations and Frameworks
ORM tools assist organizations in maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as the Basel Accords, by providing frameworks, controls, and monitoring capabilities. By automating compliance processes, documenting controls, and tracking regulatory changes, these tools help organizations demonstrate adherence to compliance obligations and enhance overall governance practices.
Competitive Advantage
By efficiently managing operational risks, you can improve decision-making, enhance compliance, and turn risks into a strategic advantage. This approach to risk management can also improve your reputation in the market, making your organization more attractive to customers, investors, and partners.
Better Efficiency
With the automation of repeatable tasks, the tool reduces the time and effort required for manual risk management activities. This frees up resources, allowing your team to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine risk management tasks. Moreover, real-time data analytics and reporting capabilities enable quicker decision-making, ensuring potential risks are addressed promptly and effectively.
Here are the key steps that organizations can follow to implement an ORM software solution:

Define Clear SOW
Start by defining a clear Statement of Work (SOW). Outline the scope, including what the ORM tool will cover and what it won't. Set realistic timelines for each phase of the implementation. Assign responsibilities to team members, ensuring everyone understands their role and deliverables.
Data Migration and Integration
Ensure that all relevant data is accurately transferred to the new system. Verify the integrity and completeness of data before going live. Additionally, focus on integrating the ORM tool with existing systems to create a unified data environment.
Training and Onboarding
Don't just drop the new tool into your organization's lap and expect people to figure it out. Develop a comprehensive training program to teach employees how the tool works and their benefits. Onboard people slowly in phases so they can get used to the tool gradually.
Project Risk Management
Identify the risks to the tool’s implementation and user adoption and draw a project risk management plan. Regularly monitor the risks and address any issues promptly. Proactive risk management ensures the smooth implementation and adoption of the tool and minimizes disruptions.
Always Optimize
Once the tool is deployed, it needs to be reviewed and upgraded to ensure it is working as intended. Monitor how people use them and look for ways to enhance the user experience. Send out surveys to get feedback on what's working and not working. This feedback can then be shared with the software provider to innovate and optimize the tool, driving more user adoption.
Ongoing Support from Vendor’s SMEs
Following the initial launch and training, organizations should engage with the software providers to not just escalate issues and provide feedback on the tool but also share knowledge, expertise, and best practices with their subject matter experts (SMEs), customer and product councils, special interest groups, etc. This will help organizations continuously improve their ORM strategy and ensure that it is aligned with industry best practices.
With technology advancing at breakneck speed, ORM tools will look very different in just a few years. Some of the most promising innovations include:
- Risk modeling algorithms: AI can analyze huge volumes of data to detect complex patterns and insights humans might miss.
- Automated risk assessments: Tedious risk assessment processes like surveys, checklists, and risk rating matrices could be automated using natural language processing. AI could review policies, incident reporting, and audit findings to detect, categorize, and score risks.
- Risk visualization dashboards: Advanced data visualization tools can translate complex risk data into intuitive, interactive dashboards. These dashboards provide a holistic view of risks across the company with drill-down capabilities to analyze risks.
MetricStream Operational Risk Management helps organizations automate and streamline operational risk processes. It is purpose-built to meet the operational risk needs of banks and financial services institutions, including a centralized risk and control library and well-defined workflows for risk and control self-assessments, loss management, KRIs tracking, issue management, and more. Graphical dashboards and powerful reports with drill-down capabilities enable risk practitioners to gain actionable risk insights and slide and dice the data to pinpoint problem areas to address them proactively.
To learn more about MetricStream Operational Risk Management (ORM) software, request a personalized demo today.
What are the top ORM tools of 2025?
Organizations contemplating which ORM tool to purchase can refer to the reports from independent research firms, including Chartis, Forrester, and Gartner. MetricStream has been named a Category Leader in all seven quadrants of the Chartis Research RiskTech Quadrant® for Integrated GRC Solutions, 2024, including Operational risk, Internal audit, Third-party risk, IT risk, Conduct risk and controls, GRC analytics, and Enterprise GRC. MetricStream was also recognized as a Leader in The Forrester Wave™: Governance, Risk, and Compliance Platforms, Q4 2023.
To learn more, read our blog “What It Takes to Be a Leader in Governance, Risk, and Compliance”, by Pat McParland, AVP of Product Marketing at MetricStream.








