Introduction
For businesses aiming to achieve long-term and sustainable success, understanding potential risks is not just advantageous—it is essential. When the board, management, and stakeholders are faced with decisions that could affect the trajectory of their enterprises, having a clear understanding of the organization’s risk appetite is crucial. It allows them to make informed choices about which opportunities to pursue and which hazards to avoid.
This article provides a deep dive into the risk appetite framework - its definition, key components, usage, benefits, and more.
Key Takeaways
- A risk appetite framework outlines the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept to achieve its objectives, guiding decision-making and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
- A comprehensive risk appetite framework includes various key components, including a risk appetite statement, risk capacity, clearly defined roles, and processes for monitoring and reporting. These elements help in setting and communicating risk boundaries within the organization.
- A risk appetite framework is used by senior executives, risk management teams, financial officers, and auditors to make informed decisions, allocate resources, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Benefits of a risk appetite framework include enhanced risk management, better alignment of operations with strategic goals, better stakeholder trust, optimized resource allocation, and improved compliance.
What is a Risk Appetite Framework?
A risk appetite framework defines the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, providing guidelines for risk management. It is an organization's guide to balancing risk and reward.
The framework helps businesses determine the amount and type of risk (e.g., financial, operational) they're willing to accept to achieve their strategic goals. It outlines policies, procedures, and structures to identify, assess, mitigate, and manage risks effectively.
A common risk language is one of the prerequisites for developing a risk appetite framework as it ensures consistent understanding for discussing risk within the organization. A risk appetite framework establishes boundaries for risk-taking and ensures that these limits are communicated effectively across all levels of the organization. This in turn helps create a consistent approach to risk management, allowing organizations to operate with a balanced perspective on risk and reward.
Risk Appetite Framework Example
To illustrate how a risk appetite framework operates in practice, consider the example of a mid-sized technology company looking to expand its market presence through the launch of a new product line. The executive team must evaluate the risks associated with this venture, including financial investment, market acceptance, and potential technological challenges.
- Risk Appetite Statement: The company’s board issues a statement indicating their willingness to accept a moderate level of risk to achieve innovation and growth, as long as potential losses do not exceed 5% of the company’s annual revenue.
- Risk Capacity
- Financial Risk Tolerance: The company sets a financial risk tolerance of $2 million for the new product development and launch, meaning they are prepared to invest up to this amount, understanding that the financial return is not guaranteed.
- Operational Risk Tolerance: They establish an operational risk tolerance that allows for a 10% increase in operational costs, acknowledging potential inefficiencies during the product rollout.
- Market Risk Tolerance: Market research must show at least a 70% probability of market acceptance before proceeding with the product launch.
- Outlining of Roles
- Board of Directors: Provides oversight and approves the risk appetite statement and tolerances.
- Risk Committee: Monitors risk levels and ensures conformity with the risk appetite framework.
- Project Team: Responsible for the day-to-day management and implementation of the new product line, ensuring that activities stay within the defined risk tolerances.
- Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Key risk indicators (KRIs) are tracked to provide early warnings of potential risks exceeding acceptable levels, such as budget overruns or delayed timelines.
Who Uses a Risk Appetite Framework?
A risk appetite framework is leveraged by a wide range of stakeholders across various levels of hierarchy in an organization. Primarily, senior executives and board members use it to guide strategic decision-making and ensure that the company’s risk-taking aligns with its overall objectives and values.
Chief risk officers (CROs) and risk management teams utilize the framework to identify, assess, and manage risks in a manner consistent with the organization’s risk tolerance and appetite. Financial officers and investment managers also use the framework to make informed decisions on capital allocation and investments, ensuring they are within acceptable risk boundaries. Additionally, internal auditors and compliance officers refer to the risk appetite framework to ensure that the organization adheres to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Components of a Risk Appetite Framework
Below are the essential components that make up a risk appetite framework:
Risk Appetite Statement
The risk appetite statement is a formal articulation of the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its strategic objectives. This statement serves as a foundational document, guiding decision-making across all levels of the organization. It encapsulates the company’s risk philosophy, providing clear directives on acceptable risk levels in various domains such as financial, operational, reputational, and compliance risks.
The risk appetite statement ensures that all stakeholders have a unified understanding of the risk boundaries, fostering a culture of informed and balanced risk-taking. It also helps in syncing the strategic objectives with risk management practices, ensuring that the organization does not undertake risks that could jeopardize its long-term sustainability.
Risk Capacity
Risk capacity refers to the maximum amount of risk an organization can absorb without compromising its operational viability and strategic goals. It is determined by analyzing various factors such as financial resources, operational capabilities, market conditions, and regulatory environment. Risk capacity acts as a critical benchmark, providing a quantitative basis for setting risk limits within the organization. By understanding its risk capacity, an organization can ensure that its risk appetite is realistic and aligned with its ability to manage potential adverse impacts.
Outlining of Roles
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are essential components of an effective risk appetite framework. Each stakeholder group within the organization must understand their specific responsibilities and how they contribute to the overall risk management process.
- The Board of Directors is responsible for setting the risk appetite and providing strategic oversight.
- Executive management translates this appetite into actionable policies and integrates it into business processes.
- Risk managers and compliance officers are tasked with identifying, assessing, and monitoring risks to ensure they stay within the established appetite.
By clearly outlining these roles, organizations can ensure cohesive and coordinated efforts in managing risks, thereby enhancing overall risk governance.
Principles of a Risk Appetite Framework
Below are four key principles that ensure its effectiveness:
- Alignment with Organizational Strategy An effective risk appetite framework must be intrinsically linked to the organization’s overarching strategy. This alignment ensures that risk-taking is purposeful and in pursuit of strategic goals. The framework should define acceptable levels of risk that the organization can take to achieve its objectives, and these should be communicated clearly to all stakeholders.
- Clear Communication and Understanding Clarity in communication is essential when implementing a risk appetite framework. All stakeholders, from executives to operational teams, must understand the organization’s risk appetite. Clear documentation and dissemination of the framework help in embedding risk culture across the organization. This principle emphasizes the importance of using unambiguous language and providing examples where necessary to illustrate acceptable and unacceptable risks.
- Dynamic and Adaptive Approach The RAF should be dynamic and adaptable to changing internal and external environments. This involves regular reviews and updates to the framework to reflect shifts in the business landscape, regulatory changes, and emerging risks. A static framework can quickly become obsolete, leading to either excessive risk-taking or overly conservative practices. A dynamic approach ensures that the organization remains resilient and responsive to new challenges and opportunities.
- Governance and Oversight This involves establishing clear roles and responsibilities for risk management activities, as well as setting up robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms. The board of directors and senior management should provide oversight to ensure that the RAF is being followed and that deviations are addressed promptly. Strong governance structures enhance accountability and ensure that risk appetite is managed effectively across the organization.
How to Develop a Risk Appetite Framework?
Developing a robust risk appetite framework requires a systematic approach that involves several key steps. Below is a step-by-step guide to help organizations create an effective RAF:
- Understand the Organization’s Strategic Objectives Begin by clearly defining the strategic goals of the organization. Understand what the organization aims to achieve and the key drivers of success. This will help you determine the level of risk the organization is willing to accept in tandem with its objectives.
- Engage Key Stakeholders Involve senior management, the board of directors, and other key stakeholders in the process. Their input is crucial in determining the organization’s risk appetite. Conduct workshops and discussions to gather diverse perspectives and ensure that there is consensus on the risk appetite levels.
- Identify and Assess Risks Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify the risks that the organization faces. Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of each risk.
- Define Risk Appetite Statements Define and document clear risk appetite statements that articulate the organization’s tolerance for different types of risks. These statements should reflect the organization’s strategic objectives and guide acceptable risk levels. For example, a risk appetite statement for financial risks might specify acceptable levels of debt or investment losses.
- Establish Risk Limits and Tolerances Based on the risk appetite statements, set specific risk limits and tolerances for different risk categories. These limits should be measurable and provide a clear threshold for acceptable risk levels. For instance, you might set a maximum acceptable loss for a particular business unit or a limit on the amount of credit risk the organization is willing to take on.
- Integrate with Risk Management Processes Ensure that the risk appetite framework is integrated with the organization’s overall risk management processes. This includes embedding the risk appetite into decision-making processes, risk assessments, and risk mitigation strategies. The framework should be a living document that evolves with the organization and its changing risk environment.
- Review and Revise Regularly Conduct regular reviews of the risk appetite framework to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This should include periodic reassessments of the organization’s risk profile, strategic objectives, and external environment. Make necessary adjustments to the risk appetite statements, limits, and tolerances based on these reviews.
Benefits of a Risk Appetite Framework
A risk appetite framework enhances risk management by setting clear thresholds, aligning daily operations with strategic goals, and providing stakeholder confidence. It optimizes resource allocation and ensures regulatory compliance, demonstrating a commitment to attentive risk management.
Here are some key benefits:
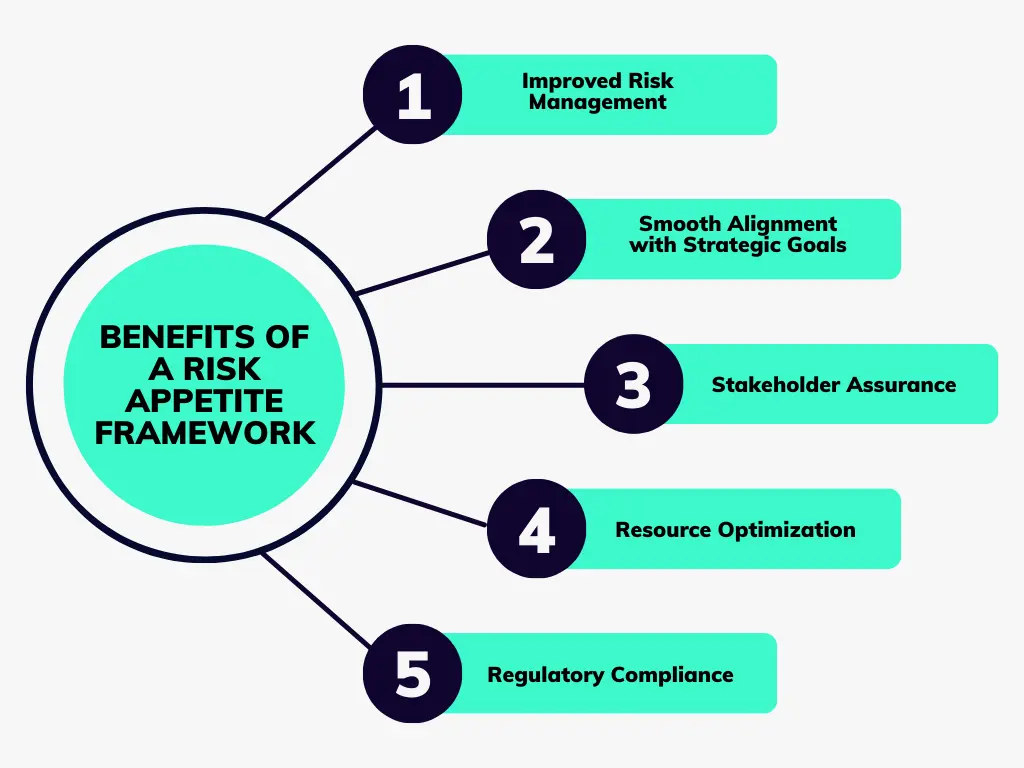
- Improved Risk Management By establishing explicit risk thresholds, organizations can proactively identify and address potential risks before they escalate. This preemptive approach helps in mitigating adverse outcomes and enhances overall risk management efficiency.
- Smooth Alignment with Strategic Goals Risk appetite frameworks ensure that all levels of the organization understand and operate within defined risk boundaries, promoting integration between daily operations and long-term strategic goals.
- Stakeholder Assurance Well-defined risk appetites provide stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and employees, with confidence that the organization is managing its risks effectively.
- Resource Optimization By understanding the acceptable levels of risk, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively. This ensures that resources are not wasted on mitigating low-priority risks and are instead focused on areas that require more attention.
- Regulatory Compliance A robust risk appetite framework aids in meeting regulatory requirements and expectations. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to prudent risk management practices, reducing the likelihood of regulatory penalties.
Conclusion
At MetricStream, we understand the intricacies involved in establishing a robust risk appetite framework. Our solutions are designed to help organizations navigate the complexities of risk management, ensuring that risks are identified, assessed, and managed in a manner that aligns with the organization’s objectives.
Adopting such a framework is a foundational element for any organization committed to achieving all its goals responsibly and sustainably.
To learn more about MetricStream Enterprise Risk Management, request a personalized demo today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are risk limits, and how do they relate to risk appetite?
Risk limits are specific thresholds set within the risk appetite framework to control exposure to various risks. They provide actionable boundaries to ensure the organization operates within its risk appetite.
What is the difference between risk appetite and risk tolerance?
Risk appetite is the overall level of risk an enterprise is willing to take to achieve its objectives, while risk tolerance is the level of variation an organization is ready to accept in outcomes related to specific risks within the broader appetite. Tolerance levels are more granular and specific.
For businesses aiming to achieve long-term and sustainable success, understanding potential risks is not just advantageous—it is essential. When the board, management, and stakeholders are faced with decisions that could affect the trajectory of their enterprises, having a clear understanding of the organization’s risk appetite is crucial. It allows them to make informed choices about which opportunities to pursue and which hazards to avoid.
This article provides a deep dive into the risk appetite framework - its definition, key components, usage, benefits, and more.
- A risk appetite framework outlines the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept to achieve its objectives, guiding decision-making and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
- A comprehensive risk appetite framework includes various key components, including a risk appetite statement, risk capacity, clearly defined roles, and processes for monitoring and reporting. These elements help in setting and communicating risk boundaries within the organization.
- A risk appetite framework is used by senior executives, risk management teams, financial officers, and auditors to make informed decisions, allocate resources, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Benefits of a risk appetite framework include enhanced risk management, better alignment of operations with strategic goals, better stakeholder trust, optimized resource allocation, and improved compliance.
A risk appetite framework defines the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, providing guidelines for risk management. It is an organization's guide to balancing risk and reward.
The framework helps businesses determine the amount and type of risk (e.g., financial, operational) they're willing to accept to achieve their strategic goals. It outlines policies, procedures, and structures to identify, assess, mitigate, and manage risks effectively.
A common risk language is one of the prerequisites for developing a risk appetite framework as it ensures consistent understanding for discussing risk within the organization. A risk appetite framework establishes boundaries for risk-taking and ensures that these limits are communicated effectively across all levels of the organization. This in turn helps create a consistent approach to risk management, allowing organizations to operate with a balanced perspective on risk and reward.
To illustrate how a risk appetite framework operates in practice, consider the example of a mid-sized technology company looking to expand its market presence through the launch of a new product line. The executive team must evaluate the risks associated with this venture, including financial investment, market acceptance, and potential technological challenges.
- Risk Appetite Statement: The company’s board issues a statement indicating their willingness to accept a moderate level of risk to achieve innovation and growth, as long as potential losses do not exceed 5% of the company’s annual revenue.
- Risk Capacity
- Financial Risk Tolerance: The company sets a financial risk tolerance of $2 million for the new product development and launch, meaning they are prepared to invest up to this amount, understanding that the financial return is not guaranteed.
- Operational Risk Tolerance: They establish an operational risk tolerance that allows for a 10% increase in operational costs, acknowledging potential inefficiencies during the product rollout.
- Market Risk Tolerance: Market research must show at least a 70% probability of market acceptance before proceeding with the product launch.
- Outlining of Roles
- Board of Directors: Provides oversight and approves the risk appetite statement and tolerances.
- Risk Committee: Monitors risk levels and ensures conformity with the risk appetite framework.
- Project Team: Responsible for the day-to-day management and implementation of the new product line, ensuring that activities stay within the defined risk tolerances.
- Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Key risk indicators (KRIs) are tracked to provide early warnings of potential risks exceeding acceptable levels, such as budget overruns or delayed timelines.
A risk appetite framework is leveraged by a wide range of stakeholders across various levels of hierarchy in an organization. Primarily, senior executives and board members use it to guide strategic decision-making and ensure that the company’s risk-taking aligns with its overall objectives and values.
Chief risk officers (CROs) and risk management teams utilize the framework to identify, assess, and manage risks in a manner consistent with the organization’s risk tolerance and appetite. Financial officers and investment managers also use the framework to make informed decisions on capital allocation and investments, ensuring they are within acceptable risk boundaries. Additionally, internal auditors and compliance officers refer to the risk appetite framework to ensure that the organization adheres to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Below are the essential components that make up a risk appetite framework:
Risk Appetite Statement
The risk appetite statement is a formal articulation of the amount and type of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its strategic objectives. This statement serves as a foundational document, guiding decision-making across all levels of the organization. It encapsulates the company’s risk philosophy, providing clear directives on acceptable risk levels in various domains such as financial, operational, reputational, and compliance risks.
The risk appetite statement ensures that all stakeholders have a unified understanding of the risk boundaries, fostering a culture of informed and balanced risk-taking. It also helps in syncing the strategic objectives with risk management practices, ensuring that the organization does not undertake risks that could jeopardize its long-term sustainability.
Risk Capacity
Risk capacity refers to the maximum amount of risk an organization can absorb without compromising its operational viability and strategic goals. It is determined by analyzing various factors such as financial resources, operational capabilities, market conditions, and regulatory environment. Risk capacity acts as a critical benchmark, providing a quantitative basis for setting risk limits within the organization. By understanding its risk capacity, an organization can ensure that its risk appetite is realistic and aligned with its ability to manage potential adverse impacts.
Outlining of Roles
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are essential components of an effective risk appetite framework. Each stakeholder group within the organization must understand their specific responsibilities and how they contribute to the overall risk management process.
- The Board of Directors is responsible for setting the risk appetite and providing strategic oversight.
- Executive management translates this appetite into actionable policies and integrates it into business processes.
- Risk managers and compliance officers are tasked with identifying, assessing, and monitoring risks to ensure they stay within the established appetite.
By clearly outlining these roles, organizations can ensure cohesive and coordinated efforts in managing risks, thereby enhancing overall risk governance.
Below are four key principles that ensure its effectiveness:
- Alignment with Organizational Strategy An effective risk appetite framework must be intrinsically linked to the organization’s overarching strategy. This alignment ensures that risk-taking is purposeful and in pursuit of strategic goals. The framework should define acceptable levels of risk that the organization can take to achieve its objectives, and these should be communicated clearly to all stakeholders.
- Clear Communication and Understanding Clarity in communication is essential when implementing a risk appetite framework. All stakeholders, from executives to operational teams, must understand the organization’s risk appetite. Clear documentation and dissemination of the framework help in embedding risk culture across the organization. This principle emphasizes the importance of using unambiguous language and providing examples where necessary to illustrate acceptable and unacceptable risks.
- Dynamic and Adaptive Approach The RAF should be dynamic and adaptable to changing internal and external environments. This involves regular reviews and updates to the framework to reflect shifts in the business landscape, regulatory changes, and emerging risks. A static framework can quickly become obsolete, leading to either excessive risk-taking or overly conservative practices. A dynamic approach ensures that the organization remains resilient and responsive to new challenges and opportunities.
- Governance and Oversight This involves establishing clear roles and responsibilities for risk management activities, as well as setting up robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms. The board of directors and senior management should provide oversight to ensure that the RAF is being followed and that deviations are addressed promptly. Strong governance structures enhance accountability and ensure that risk appetite is managed effectively across the organization.
Developing a robust risk appetite framework requires a systematic approach that involves several key steps. Below is a step-by-step guide to help organizations create an effective RAF:
- Understand the Organization’s Strategic Objectives Begin by clearly defining the strategic goals of the organization. Understand what the organization aims to achieve and the key drivers of success. This will help you determine the level of risk the organization is willing to accept in tandem with its objectives.
- Engage Key Stakeholders Involve senior management, the board of directors, and other key stakeholders in the process. Their input is crucial in determining the organization’s risk appetite. Conduct workshops and discussions to gather diverse perspectives and ensure that there is consensus on the risk appetite levels.
- Identify and Assess Risks Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify the risks that the organization faces. Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of each risk.
- Define Risk Appetite Statements Define and document clear risk appetite statements that articulate the organization’s tolerance for different types of risks. These statements should reflect the organization’s strategic objectives and guide acceptable risk levels. For example, a risk appetite statement for financial risks might specify acceptable levels of debt or investment losses.
- Establish Risk Limits and Tolerances Based on the risk appetite statements, set specific risk limits and tolerances for different risk categories. These limits should be measurable and provide a clear threshold for acceptable risk levels. For instance, you might set a maximum acceptable loss for a particular business unit or a limit on the amount of credit risk the organization is willing to take on.
- Integrate with Risk Management Processes Ensure that the risk appetite framework is integrated with the organization’s overall risk management processes. This includes embedding the risk appetite into decision-making processes, risk assessments, and risk mitigation strategies. The framework should be a living document that evolves with the organization and its changing risk environment.
- Review and Revise Regularly Conduct regular reviews of the risk appetite framework to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This should include periodic reassessments of the organization’s risk profile, strategic objectives, and external environment. Make necessary adjustments to the risk appetite statements, limits, and tolerances based on these reviews.
A risk appetite framework enhances risk management by setting clear thresholds, aligning daily operations with strategic goals, and providing stakeholder confidence. It optimizes resource allocation and ensures regulatory compliance, demonstrating a commitment to attentive risk management.
Here are some key benefits:

- Improved Risk Management By establishing explicit risk thresholds, organizations can proactively identify and address potential risks before they escalate. This preemptive approach helps in mitigating adverse outcomes and enhances overall risk management efficiency.
- Smooth Alignment with Strategic Goals Risk appetite frameworks ensure that all levels of the organization understand and operate within defined risk boundaries, promoting integration between daily operations and long-term strategic goals.
- Stakeholder Assurance Well-defined risk appetites provide stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and employees, with confidence that the organization is managing its risks effectively.
- Resource Optimization By understanding the acceptable levels of risk, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively. This ensures that resources are not wasted on mitigating low-priority risks and are instead focused on areas that require more attention.
- Regulatory Compliance A robust risk appetite framework aids in meeting regulatory requirements and expectations. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to prudent risk management practices, reducing the likelihood of regulatory penalties.
At MetricStream, we understand the intricacies involved in establishing a robust risk appetite framework. Our solutions are designed to help organizations navigate the complexities of risk management, ensuring that risks are identified, assessed, and managed in a manner that aligns with the organization’s objectives.
Adopting such a framework is a foundational element for any organization committed to achieving all its goals responsibly and sustainably.
To learn more about MetricStream Enterprise Risk Management, request a personalized demo today.
What are risk limits, and how do they relate to risk appetite?
Risk limits are specific thresholds set within the risk appetite framework to control exposure to various risks. They provide actionable boundaries to ensure the organization operates within its risk appetite.
What is the difference between risk appetite and risk tolerance?
Risk appetite is the overall level of risk an enterprise is willing to take to achieve its objectives, while risk tolerance is the level of variation an organization is ready to accept in outcomes related to specific risks within the broader appetite. Tolerance levels are more granular and specific.








